Master the 5S Workplace: Boost Efficiency & Organization Today.
Are you wondering how to boost your workplace’s efficiency and organization? The 5S workplace methodology is here to help. This article will explain the five key steps of 5S, its benefits, and actionable tips for implementation. Let’s dive in and transform your workspace!
Key Takeaways
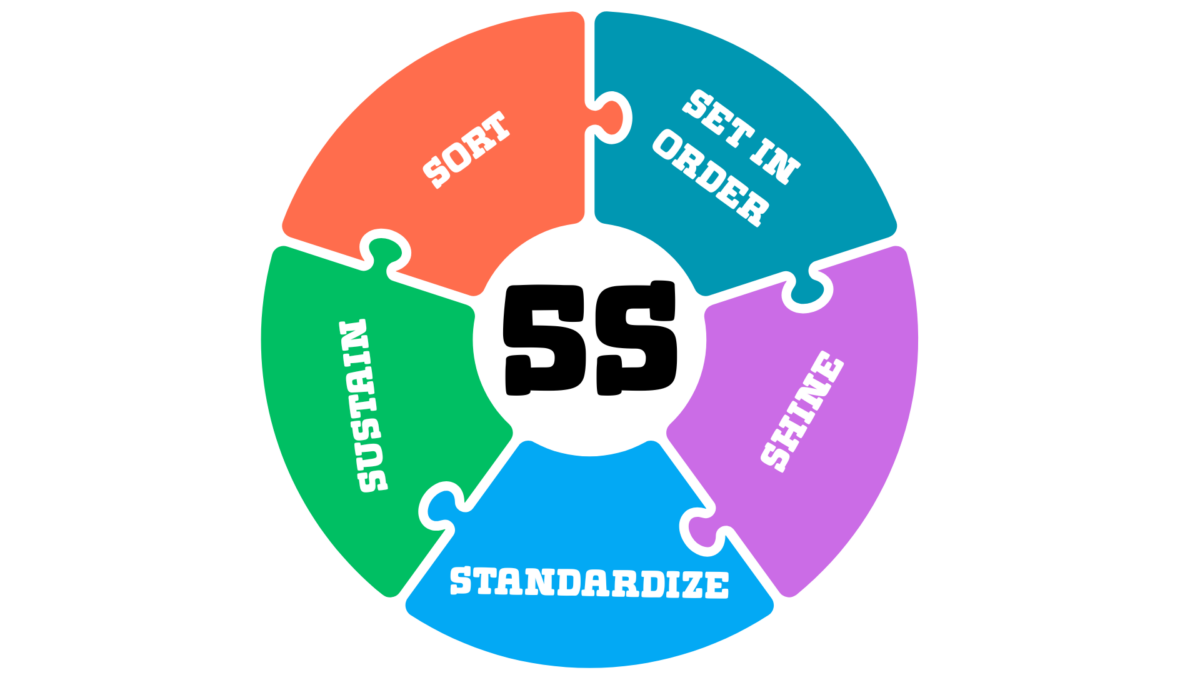
- The 5S methodology consists of five steps: sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and sustain. It aims to enhance workplace efficiency and organization.
- Implementing 5S requires active employee participation and commitment, as well as strategies for overcoming resistance to change to ensure success.
- Benefits of 5S include improved workplace safety, increased efficiency and productivity, and enhanced employee morale, making it a valuable practice for various industries.
Introduction to 5S
The 5S methodology is a cornerstone for organizations seeking to optimize workplace efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance compliance with industry standards. Rooted in the Toyota Production System, this five-step methodology—Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain—has revolutionized the manufacturing industry and beyond. By systematically organizing tools and materials, eliminating unnecessary motion, and creating a visual workplace, 5S empowers teams to streamline production processes and maintain high workplace safety.
Implementing 5S transforms chaotic work areas into clean, organized, efficient environments. This reduces wasted time and unnecessary items and boosts employee morale by fostering a sense of pride and ownership. The visual cues and structured processes inherent in the 5S methodology make it easier for employees to locate tools, follow safety protocols, and contribute to a culture of continuous improvement. As a result, organizations experience smoother operations, higher productivity, and a safer, more engaging workplace for everyone involved.
If you want to deepen your knowledge of practical 5S implementation, sign up for the 5S Fundamentals Course.
Understanding the 5S Methodology
At its core, the 5S methodology is a five-step approach that focuses on workplace efficiency and organization. This method consists of:
- Sort
- Set in Order
- Shine
- Standardize
- Sustain. Each step addresses disorganization and improves efficiency, transforming cluttered spaces into productivity models.
The primary goal of 5S is to eliminate waste, foster a culture of quality, and enhance overall productivity. By creating a more organized and efficient environment, 5S directly improves business operations and supports overall organizational effectiveness. The key steps include:
- Systematically sorting through items
- Organizing them
- Cleaning the workspace
- Standardizing processes
- Sustaining these practices. These actions can significantly boost workplace efficiency and, as a lean manufacturing tool, 5S reduces waste throughout the organization.
Implementing 5S leads to a cleaner, more organized work environment and enhances worker safety and quality. This methodology has been proven effective in various industries, making it a versatile tool for any organization looking to implement 5S in its operations.
The Origins of 5S and Lean Manufacturing
The 5S methodology emerged as a crucial component of the Toyota Production System, developed to enhance workplace organization and eliminate waste. The Toyota Motor Company pioneered the 5S methods as part of its drive for manufacturing excellence. Taiichi Ohno, often regarded as the father of the Toyota Production System, played a pivotal role in refining these principles. Alongside Ohno, Shigeo Shingo contributed significantly by training Toyota engineers and further developing the 5S methodology.
The 5S approach was initially designed to improve agility and minimize waste within Toyota’s operations. This methodology laid the foundation for lean manufacturing, a broader philosophy aimed at increasing value by eliminating waste. 5S is key to achieving manufacturing excellence through improved productivity, safety, and quality. The term ‘lean production’ was later popularized by the book ‘The Machine that Changed the World,’ highlighting Toyota’s groundbreaking methods.
Implementing the 5S methodology has proven effective beyond Toyota’s manufacturing floors. Many companies worldwide adopt these principles to enhance operational efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product quality. Takashi Osada’s first English-language book on 5S, published in 1991, introduced these core principles to Western audiences, further solidifying its global impact.
Implementing 5S in Your Workplace
Implementing 5S involves more than just following steps; it requires active participation and commitment from all employees. Understanding and preparing for the changes ahead is crucial. Below are practical tips and strategies for each step to ensure successful implementation.
Engaging employees in the 5S process helps overcome resistance to change and ensures long-term success. Key strategies include:
- Establishing baseline performance measurements
- Creating simple informational materials to help employees understand and apply 5S practices
- Providing adequate resources and tailored training
With these approaches, organizations can enjoy improved workplace organization and efficiency and new, cost-effective ideas for organizing workplaces.
Want to apply 5S effectively in your business? Enroll in: 5S Workplace Efficiency Program.
Step 1: Sort (Seiri)
The first step in the 5S methodology, Sort (Seiri), involves separating and categorizing items based on their usefulness. The goal is to eliminate clutter and make the workspace more productive and efficient. A common technique used during this phase is the red tag method, where items that are not immediately necessary or deemed unnecessary are tagged with red tags and removed after a set period if not used, a process often referred to as red tagging. The remaining items are organized and arranged to optimize efficiency and support Lean practices.
Dedicating a specific timeframe for sorting allows organizations to systematically evaluate the necessity of each item, ensuring that only useful tools remain in the workspace. This process reduces clutter and enhances overall productivity by creating a more organized environment.
Step 2: Set in Order (Seiton)
The second step, Set in Order (Seiton), systematically organizes items to ensure efficient storage and easy access. This involves designing a specific home for each item, allowing workers to quickly find and return tools and materials.
A key element of this phase is arranging items based on the frequency of use and logical task sequences, which helps create a more streamlined workflow. Proper organization significantly reduces the time searching for tools and materials, improving efficiency. An effective organization opens space for strategic use, improves production efficiency, and reduces wasted time.
Step 3: Shine (Seiso)
Shine (Seiso) is the third step in the 5S methodology, emphasizing thorough cleaning and routine maintenance of tools and equipment. This involves regular activities like sweeping, mopping, and putting tools away, which help maintain a clean and orderly work area.
Regular cleaning keeps work areas tidy and allows employees to inspect equipment and identify potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. Color-coding cleaning tools can further streamline this process, making it easier for workers to find and use the correct tools.
Cleanliness in the workplace directly boosts employee morale and job satisfaction. Empowering employees to take responsibility for their work areas fosters a sense of ownership and pride in maintaining a clean and efficient workspace.
Step 4: Standardize (Seiketsu)
The fourth step, Standardize (Seiketsu), aims to capture best practices and systematize them into standardized work. This involves documenting procedures to ensure that the first three steps of 5S are consistently maintained. Creating standardized procedures ensures that desired changes remain in place throughout the organization.
Standardizing 5S practices embeds these activities into daily routines, transforming them into habits. Initially, reminders about 5S tasks may be necessary, but these practices will become second nature to employees over time.
Step 5: Sustain (Shitsuke)
The final step, Sustain (Shitsuke), focuses on maintaining the standards established in the previous steps through continuous improvement and self-discipline. Ongoing training, regular audits, and inspections are necessary to ensure compliance and quality control to standardize and sustain areas for improvement.
Leadership plays a critical role in sustaining 5S practices. Company leaders must:
- Actively participate in 5S initiatives to demonstrate their importance and encourage employee acceptance.
- Conduct routine inspections and audits to prevent falling back into old habits.
- Ensure that 5S practices remain a part of the company culture.
Fostering a continuous improvement and self-discipline culture significantly improves employee engagement, satisfaction, and overall operational efficiency.
Benefits of a 5S Workplace
Implementing the 5S methodology offers numerous benefits, making it a foundational practice for lean manufacturing. These benefits include:
- Higher quality products and services
- Lower costs
- Faster operations
- Happier employees
5S also contributes to smooth operations by ensuring order and coordination in the workplace, which helps maintain optimal performance.
Almost any company can benefit from 5S, especially those focused on efficiency, safety, and reducing waste.
Specific benefits of a 5S workplace include enhanced safety, increased efficiency and productivity, and improved employee morale, which provide many benefits.
Master the practical steps of 5S implementation by joining: 5S Training for Organizations.
Enhanced Workplace Safety
One key benefit of the 5S methodology is enhanced workplace safety. Eliminating hazards and organizing items ergonomically reduces the risk of accidents and injuries. Proper management of raw materials within the 5S method is essential, as disorganized raw materials can cause accidents; correctly organizing and storing raw materials enhances safety and reduces the risk of incidents. Regular cleaning and inspections help identify potential hazards before they become safety hazards, further contributing to a safer work environment.
In addition, floor markings and visual cues can define work areas and hazardous zones on the manufacturing and shop floors, improving overall patient safety and organization. In healthcare settings, adopting 5S enhances safety and reduces patient wait times through organized workspaces and minimal clutter.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The 5S methodology significantly improves efficiency and productivity by streamlining operations and eliminating waste. By reducing the need for duplicate tools and improving inventory management, 5S helps lower operational costs and optimize resource use.
Effective layout design and visual communication of process flows reveal bottlenecks, improve workflow, reduce wasted time, and enhance overall productivity. Integrating streamlined operations with cost optimization creates a more efficient and productive work environment, particularly in a visual factory and production processes.
Improved Employee Morale
A clean, organized workplace fosters a positive work culture and boosts employee morale. Recognition of employee efforts through awards and success stories reinforces the importance of maintaining 5S standards and significantly enhances morale.
Involving employees in the 5S process and acknowledging their contributions builds a supportive work environment that encourages continuous improvement and high performance.
Visual Management Tools in 5S
Visual management tools are essential in sustaining 5S practices and maintaining standards within the visual workplace. Color-coded visual cues, schedules, and clear labels communicate processes and ensure everyone understands the organization’s standards through visual controls.
Tools like shadow boards indicate the placement of tools and highlight missing tools, while kaizen foam helps organize tool drawers for proper returns. Utilizing these visual management tools is crucial for sustaining 5S practices and improving operational efficiency.
Overcoming Challenges in 5S Implementation
Implementing 5S can be challenging. Understanding common obstacles and strategies to overcome them is key to success. One major challenge is securing executive buy-in and visible support from top management, which is essential for aligning the 5S strategy with overall business objectives.
Employee resistance can hinder 5S implementation. Employee involvement and engagement are crucial for building participation, overcoming this resistance, and ensuring a successful transition.
Designating a core management team to manage 5S strategies effectively and conducting regular audits and performance measurements can help track the effectiveness of 5S practices and maintain momentum.
Case Studies: 5S in Action
Real-world examples of 5S implementation demonstrate its tangible benefits across various industries. Companies that have successfully adopted the 5S system pioneered by Toyota include:
- Boeing
- Hewlett-Packard
- Nike
- Harley-Davidson
- Caterpillar
- Ford
These companies have significantly enhanced their operational efficiency and product quality.
In the hospitality industry, 5S maximizes resource use, increases customer satisfaction, and improves operational efficiency, showcasing the versatility and effectiveness of this methodology beyond traditional manufacturing settings.
Best Practices for Sustaining 5S
Sustaining 5S practices requires:
- Strong leadership commitment
- Regular audits
- Clear communication channels
- Recognizing and rewarding employee efforts to motivate active engagement
- Flexibility in practices to help organizations adapt to evolving business needs.
Consistency in applying 5S principles across all departments is vital for overall effectiveness, ensuring that the benefits of 5S are realized throughout the organization.
Measuring Success in Your 5S Journey
Tracking the progress and effectiveness of your 5S implementation is essential for sustaining improvements and driving continuous improvement across your organization. A key element in this process is conducting regular audits, which help ensure that 5S standards are consistently applied and that the workplace remains clean, organized, and safe. Visual controls—such as shadow boards, floor markings, and clear labels—play a vital role in making tools and materials easily accessible, highlighting missing tools, and reinforcing proper organization.
To measure the impact of your 5S journey, organizations should monitor metrics like reduced waste, increased productivity, and higher levels of employee engagement. These indicators reflect the success of your 5S implementation and highlight areas where further improvements can be made. In many industries, from manufacturing to healthcare, these practices contribute to enhanced safety and, in the case of healthcare, improved patient safety.
By regularly reviewing audit results and engaging employees in the process, organizations can identify opportunities to reduce waste further and optimize processes. This commitment to ongoing assessment and adjustment ensures that 5S remains integral to your company culture, driving excellence and efficiency in every aspect of your operations.
Summary
In conclusion, the 5S methodology is a powerful tool for transforming workplace efficiency and organization. By following the five steps—Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain—organizations can eliminate waste, enhance productivity, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. The origins of 5S within the Toyota Production System highlight its effectiveness in reducing waste and improving operational efficiency, making it a foundational practice for lean manufacturing.
Implementing 5S involves engaging employees, securing management buy-in, and utilizing visual management tools to maintain standards. Overcoming challenges and sustaining 5S practices require strong leadership, regular audits, and consistent application across all departments. By adopting 5S, organizations can achieve significant benefits, including enhanced workplace safety, increased efficiency and productivity, and improved employee morale. Embrace the 5S methodology today and unlock the full potential of your workplace.
If you’re looking for a hands-on, actionable resource for implementing 5S in your organization, don’t miss the 5S Workplace Organization course. This course provides practical steps, templates, and real-world examples to help you organize your workplace efficiently. 👉 Check it out here.
Look at a sample lesson from the practical course on implementing 5S principles in an organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the five steps of the 5S methodology?
The five steps of the 5S methodology are Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. Implementing these steps can significantly enhance efficiency and organization in the workplace.
How does 5S improve workplace safety?
5S enhances workplace safety by systematically eliminating hazards, ergonomically organizing tools and materials, and encouraging regular cleaning and inspections to proactively identify and address potential safety risks.
Can 5S be implemented in industries other than manufacturing?
Yes, 5S can be effectively implemented in industries beyond manufacturing, such as healthcare and hospitality, enhancing resource utilization and operational efficiency.
What role do visual management tools play in 5S?
Visual management tools are crucial in 5S as they enhance communication, maintain standards, and support the sustainability of 5S practices through transparent labels, color-coded cues, and organized displays.
What are some common challenges in implementing 5S, and how can they be overcome?
Implementing 5S often faces challenges such as securing executive buy-in, employee resistance, and unclear direction. These hurdles can be effectively addressed by obtaining visible support from top management, actively engaging employees, establishing a core management group, and performing regular audits and performance evaluations.
