Spis treści
Sabat Consulting consulted Jan Sabat to ensure that articles met our editorial standards.
Are you an operations manager whose operations are trapped in excessive costs and inefficiencies?
Do you struggle as a business leader to improve and deliver customer value? You are not alone, many businesses face these challenges of waste, delays and unsatisfied customers. That is where lean thinking will make the difference. Whether you are business leader or an operation manager, or a student aiming to master the lean principles through lean manufacturing training courses.
Let’s explore the practical and proven approach that lean thinking offers to increase efficiency and cut waste.
One of the most effective and powerful tools to achieve this is lean thinking, but first, let’s understand the definition of lean production. The lean thinking tool was developed in 1950s in the post-war era to respond to the limited resources and increased need for efficiency. By focusing on the elimination of inefficiencies and continuously improving processes. Toyota completely revolutionized manufacturing and created a global standard for operational excellence.
Initially, lean was designed to help manufacturers to efficiently utilize the available resources without compromising the quality. But, today its influence reaches far beyond manufacturing shaping practices across the departments and industries. Lean is more than just a set of tools it is a mindset that focuses on value maximization with minimal waste ensuring all the actions contributes to the desired outcome.
Why lean Matters Today: Overcoming Modern Business Challenges
In today’s rapidly changing and competitive world, businesses are under constant pressure to deliver high quality products and services at minimum cost and quicker response times. Lean ensures higher quality, increased efficiency, reduced costs and waste. At the heart of lean mindset are five principles that shape the idea of how organizations can improve their processes, eliminate waste and drive growth.
An Overview of Lean Operation Principles
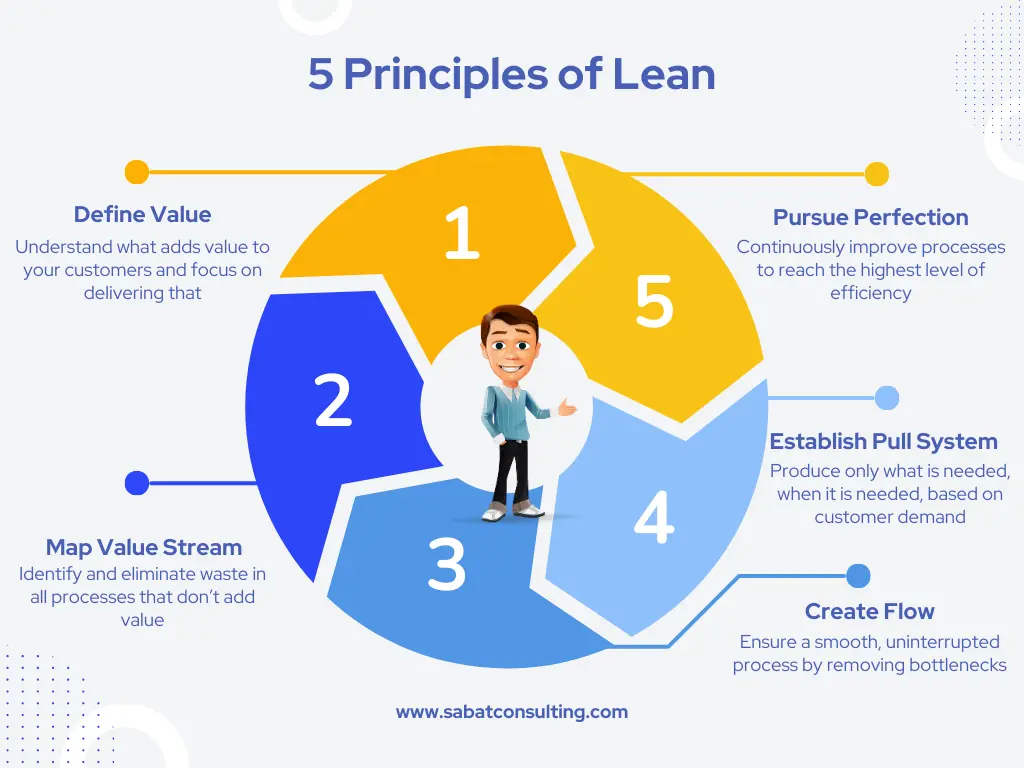
The five principles of lean are basically interconnected steps that creates a roadmap to comprehensive lean business transformation.
- Define Value
- Map value stream
- Create Flow
- Establish Pull System
- Pursue Perfection
Principle 1: Define Value
Understanding Value from the Customer’s Perspective
Any story of a successful business begins with a simple yet a powerful question “what do our customers truly values”. In lean thinking this is not just an option but the first and most important principle understanding value from the perspective of the customer. Value is what the customers are willing to pay whether it’s the fair price compared to the competitors or features that solve their problems or fast delivery.
Identifying Value Added Activities
In the light of lean thinking it is very important to discover the actual needs of the customers because many businesses face the danger of internal assumptions. Assumption that they know what their customers want instead of understanding what their customers actually values. The idea of lean thinking teaches us that not all activities created are equal as activities falls under two categories i.e. Value adding and non-value adding activities. The value-added activities are clearly noticed by the customers as it transforms the products in an effective way.
A Step by Step Guide How to Define Value
Step 1: Identify your Customer Segments
Break down your target market and customer segments into different groups based on their shared interests (For example: budget-conscious, convenience enthusiasts and premium product buyers).
Step 2: Conduct Customer Research
Conduct reviews, feed analysis, interviews and surveys to clearly identify customer needs and what they truly value.
Step 3: Translate Customer Neds into Specific Products
Convert the identified needs of the customer in the second step into measurable products and services (For example: if a customer says “I want quick response”, define it as a 24/7 effective customer response service).
Step 4: Differentiate Between Value-Adding and Non-Adding Activities
Map the process and clearly identify and label value adding activities and separate the non-value adding activities (For example: ask your self “ does this step change the product or services in a way the customer needs or values)
Jan Sabat
Principle 2: Map the Value Stream
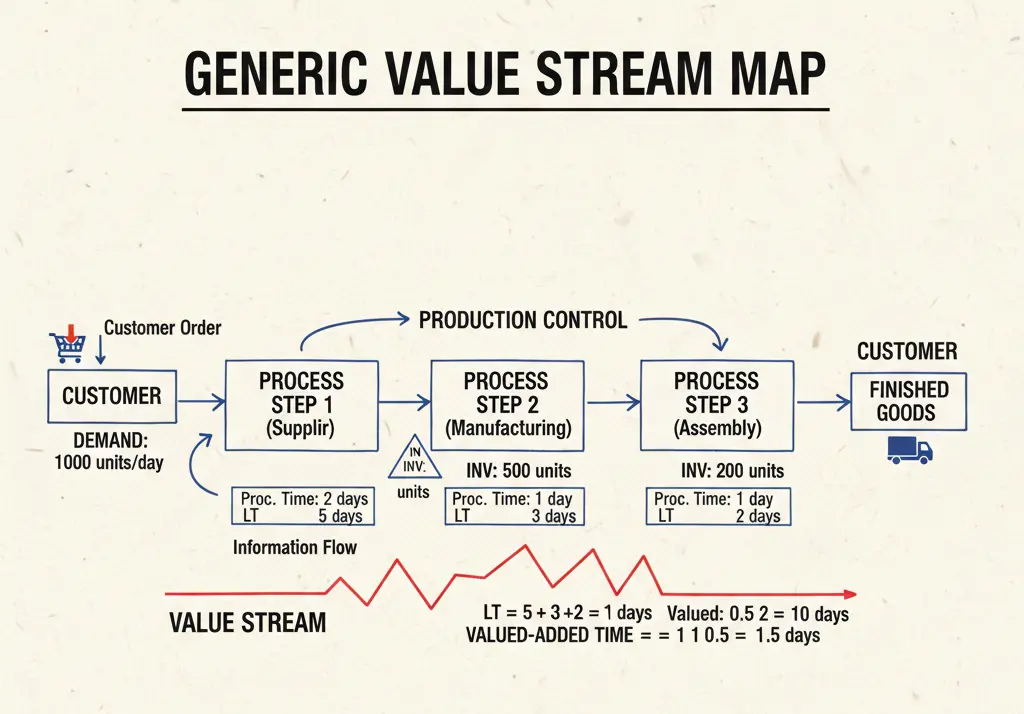
What is Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
In the journey of business transformation, after defining what your customer values the next principle is to map the value stream. This principle deals with the idea of identifying how the work flows across the business, how the resources are spent and products/services move from start to finish and where process may waste time and slow down.
The value stream mapping is basically a visual diagram that presents the entire journey of raw material, activities and information required to deliver the desired products and services. The main purpose of this principle is to highlight the value-added activities and identify bottlenecks and eliminate the waste that will lead to smart and effective practices.
How to Map the value stream: Practical Steps
Step 1: Choose a Product Family or Service
Focus on one single product or services as focus on many products at one time can be highly overwhelming.
Step 2: Walk the Process (Gemba Walk)
The next step is to go to the real place(Gemba) to learn and improve the processes and identify the waste. As it supports faster improvements and provides a frontline insight into every step from customer request to delivery.
Step 3: Draw the Current State Map
In this step focus on illustrating material flow and information flow by adding supporting information about the lead time, inventory levels, process times and rate of errors. This step will provide a baseline view of how processes are carried out.
Step 4: Identify Waste and Bottlenecks
In this step focus on identifying wastes and bottlenecks through the lean categories of waste Muda (Waste), Mura (unevenness) and Muri (overburden). Here you can identify waiting time spots, improvement areas and areas where employees struggle due to weak process design.
Step 5: Design the Future State Map
Redesign the process without inefficiencies, delays and unnecessary narrowing your improvement target.
Step 6: Create an Implementation Plan
This step you should focus on translating the future goals into a actionable and achievable steps. During this step, set short goals, assign responsibilities, set timeline and prioritize changes with high impact.
Common Challenge in VSM & How to Overcome Them?
The value stream mapping(VSM) is a game-changer for efficiency but it’s not always a smooth process. As many organizations face challenges while trying to put this tool into practice. However, most of the challenges have effective solutions. Let’s identify the most common challenges and how businesses can overcome them.
Challenge 1: Overwhelmed by Complexity or Scope Creep
The businesses may feel buried under complex data points and processes and they may want to map everything at once. This can lead to complexity and frustration in the team.
Solution: To deal with this issue, businesses should focus on starting small, choosing one product or service with the largest impact area. By using clear boundaries and narrowing the scope, businesses will see faster results.
Challenge 2: Resistance from Employees or Departments
In the face of transformation resistance to change is a common challenge. As, employees and departments can consider value stream mapping as a threat and assume it to be a blaming game rather than improvement. The resistance to change leads to slow processes and setbacks.
Solution: To overcome this challenge the businesses should focus on including frontline workers on in the process from the start. Making it clear that VSM is not about blaming but improving the working processes and make the customer experience better.
E-E-A-T Consideration:
Value Adding vs Non-Adding Activities
| Activity type | Description | Example |
| Value-added activity | This is a type of activity that increases the worth of a product or service. | Designing a user-friendly interface based on the customer feedback and value |
| Non-value-added activity | These are types of activities that utilize time and resources without adding any value to the products or service. | Long waiting time for raw material and excessive approvals without any purpose. |
| Necessary but NVA | Activities that are non-value added in the customer perspective but are important for the current process. | The project time tracking and internal reporting that is important for the management but not add value to the customer directly. |
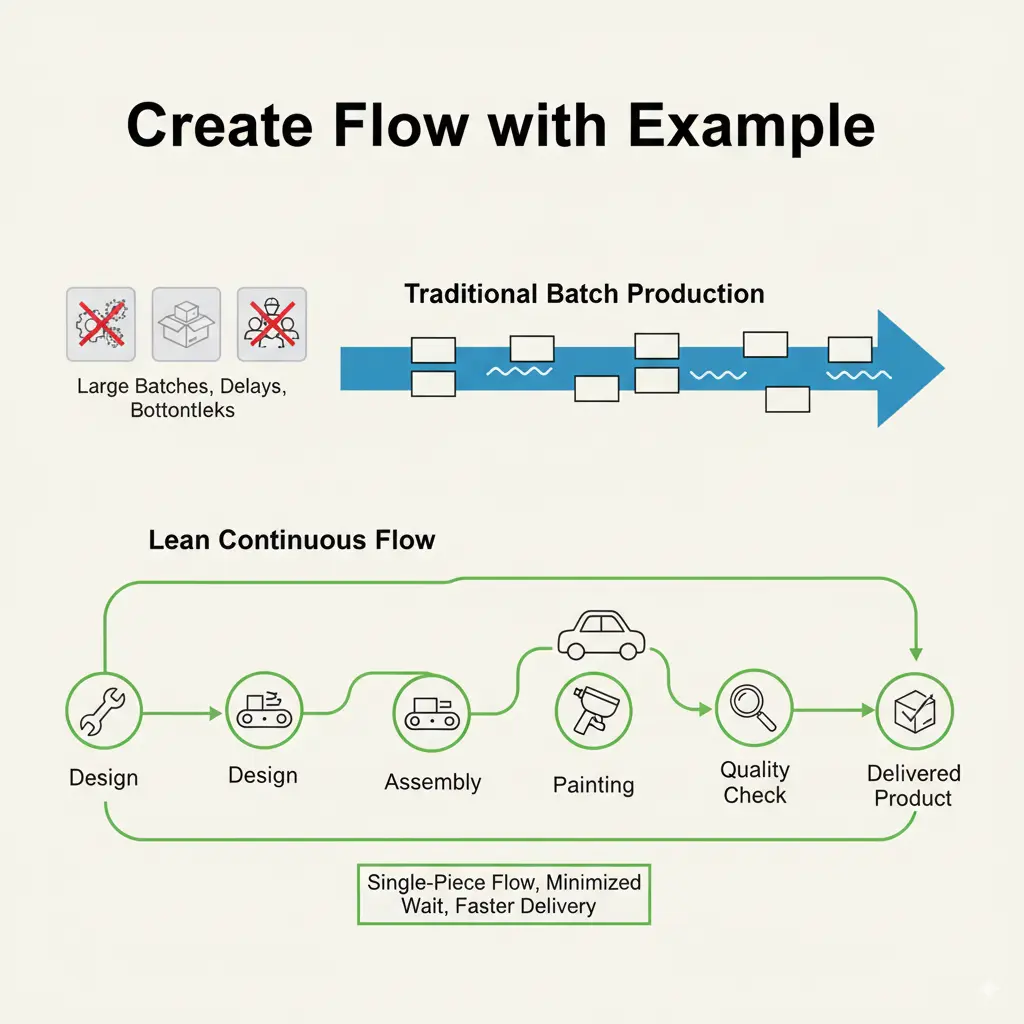
Principle 3: Create Flow
After value stream mapping the next principle is to create flow. The goal of this principle is to move products or services through the value stream without any interruption and delays. Why flow matters Ensuring smooth flow of activities is important because it identifies the problems faster, reduce lead times and inventory. As, the continuous flow will reduce the inefficiencies and enhance the overall productivity.
Steps by Step Guide How to Create Flow
Step 1: Eliminate interruptions
To ensure smooth flow it is important to identify and eliminate interruptions. This step is crucial for identifying and solving the root causes of slowdowns. For example, prevent machine breakdowns through regular maintenance, ensure material availability and address quality issues.
Step 2: Breaking Down the steps
To avoid the complexities associated with processing large batches it is effective to break them down into small and manageable batches. This step will keep the work moving and make it easier to identify problems timely.
Step 3: Reconfigure Layouts
In this step design the workplace in a way that processes flow naturally for example by grouping related tasks and co-locating placing teams.
Step 4: Balancing Workloads
To ensure smooth flow balancing workloads is an important element. Through this step level out the product mix and production volume avoiding peaks and variations in the demand. Balancing workloads will prevent overburdening teams and prevents blockages.
Step 5: Implement visual management
Through the help of tools such as dashboards and process maps makes the problems visible so they are difficult to ignore. As, these tools clearly shows blockages, delays and enables the team to collaborate on solutions.
Barriers to Flow and How to Overcome them?
Challenge: Batching due to machine setup times or departmental silos
Across the industries, large batches are produced as departments works independently and machines might take long time to step up. For example, an apparel company might run 10,000 copies of an article before shifting to another to save the step-up time. This might seem an efficient strategy but in reality in leads to delay and high inventory.
Fixations
Single-Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) This a lean tool that is used to reduce the machine set up times from hours to minutes with quick change overs. Through this tool businesses can produce small batches more regularly.
Cross-functional teams: To reduce the miscommunication and break down the silos by group employees from various departments. This will ensure strong communication and faster handoffs.
Cross-training employees: This a crucial solution to this challenge as staff trained to handle multiple tasks increases flexibility and smooth flow of processes.
Challenge: Uneven workload distribution
Uneven workloads also known as mura in lean is a serious challenge in creating flow. As, when one workstation is overloaded while others sit shiftless that leads to blockage. For instance, in a software development company, the developers may design and produce code fasters than testers can test it. This might lead to workloads and overburden on the testers while the developers run out of tasks.
Solution
Load balancing (Heijunka): To deal with this challenge it is effective to implement load balancing (Heijunka) which includes leveling of the production schedules to avoid demand peaks and variation. For example, divide the orders processing evenly across the week.
Takt Time: Takt time is an effective strategy to harmonize production with customer demand. It is basically a beat of customer demand that can be calculated by dividing the current production time by customer demand. The alignment of takt time and processes ensures that works flows evenly without overburdening each team.
Flexible Staffing: To deal with uneven workload distribution it is important to implement the strategy of flexible staffing. Through flexible staffing cross train, the employees so if one area is overloaded employees can temporarily be reassigned to other area creating a balanced workflow.
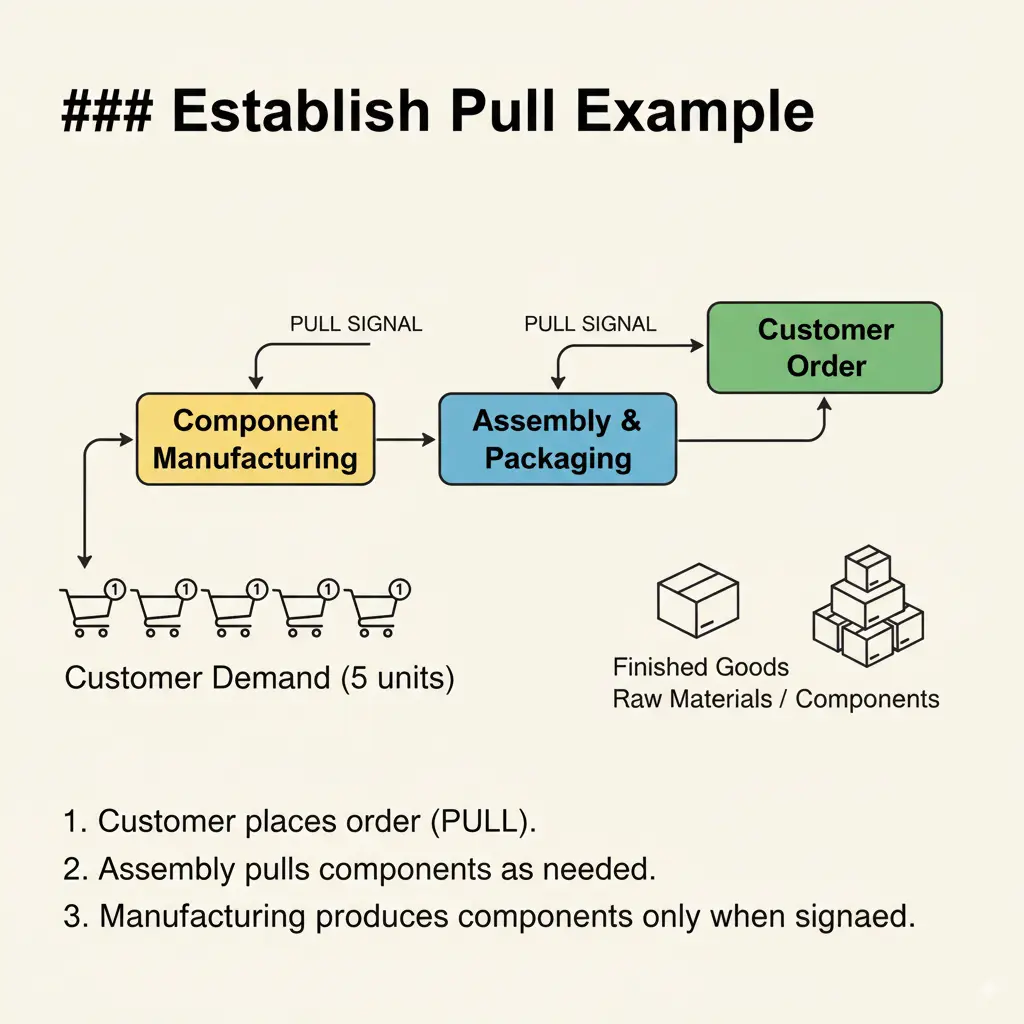
Principle 4: Establish Pull
Push vs Pull system: The pull system in lean is producing products and starting working when there is actual demand. Unlike, push system in which production is based on the future demand and large-scale production is conducted in advance. In comparison to pull the push systems leads to excess waste and inventory.
Why it matters: Establishing a pull-based system limits the inventory and work in process item while ensuring smooth flow of work. The pull-based system allows just-in-time delivery along with production of products according to the customer needs.
Implementation tool: To implement pull based system various tools such as kanban boards are used. As, it makes the implementation of pull system easier in production knowledge and work.
How to Establish Pull? Step by Step Guide
Step 1: Understanding customer Demand Patterns
Before establishing pull system, it is important to understand what and when customers need a product. This can be done through analyzing sales records, product request or seasonal demand raise. The comprehensive study of demand patterns, one can avoid overproduction.
For example, a clothing brand reviews their sales history of last three years and identifies that demand increases during the holiday season. Due to which they plan ahead and only increase production during holiday season.
Step 2: Implement Pull System
As, pull system relies on signals that demands actions when something is needed. For which Kanban boards is an effective tool that visually represent the work stages i.e. To Do, In-progress and Done. Through Kanban board managers can put WIP limit on every stage or across the board to avoid overloading. Kanban as a tool reduces waste and make the processes more flexible.
For example, Amazone use pull systems in their warehouses to restock the products based on previous sales history instead of overfilling their shelves.
Step 3: Match production with Demand
Match production with the demand to smooth out the process and reduce costs. Adjust your procurement and distribution process to ensure direct response to customer orders rather than relying on future demands.
Step 4: Avoid Overproduction
Avoid overproduction produce what is needed by customers. This will significantly cut down the excessive inventory which a major source of waste across industries.
Challenges in Pull & How to Overcome them
Challenge 1: Unpredictable Customer Demand
Significant fluctuations in the customer demand (Rise or drop) making it difficult to harmonize production with actual demand. This fluctuation can lead to shortages or excess waste(inventory).
Solution: Ensure effective use of real-time demand tracking, previous sales analytics and implement flexible scheduling. To deal with this challenge implement certain safety buffers for highly flexible demand items while keeping pull system.
Challenge 2: Long Supplier Lead Team
If the internal processes efficiently follow the pull system delays from supplier can cause delay and bottlenecks in production.
Solution: Focus on building close supplier relationships, Timely share the demand signals and adopt the strategy of just-in-time partnership.
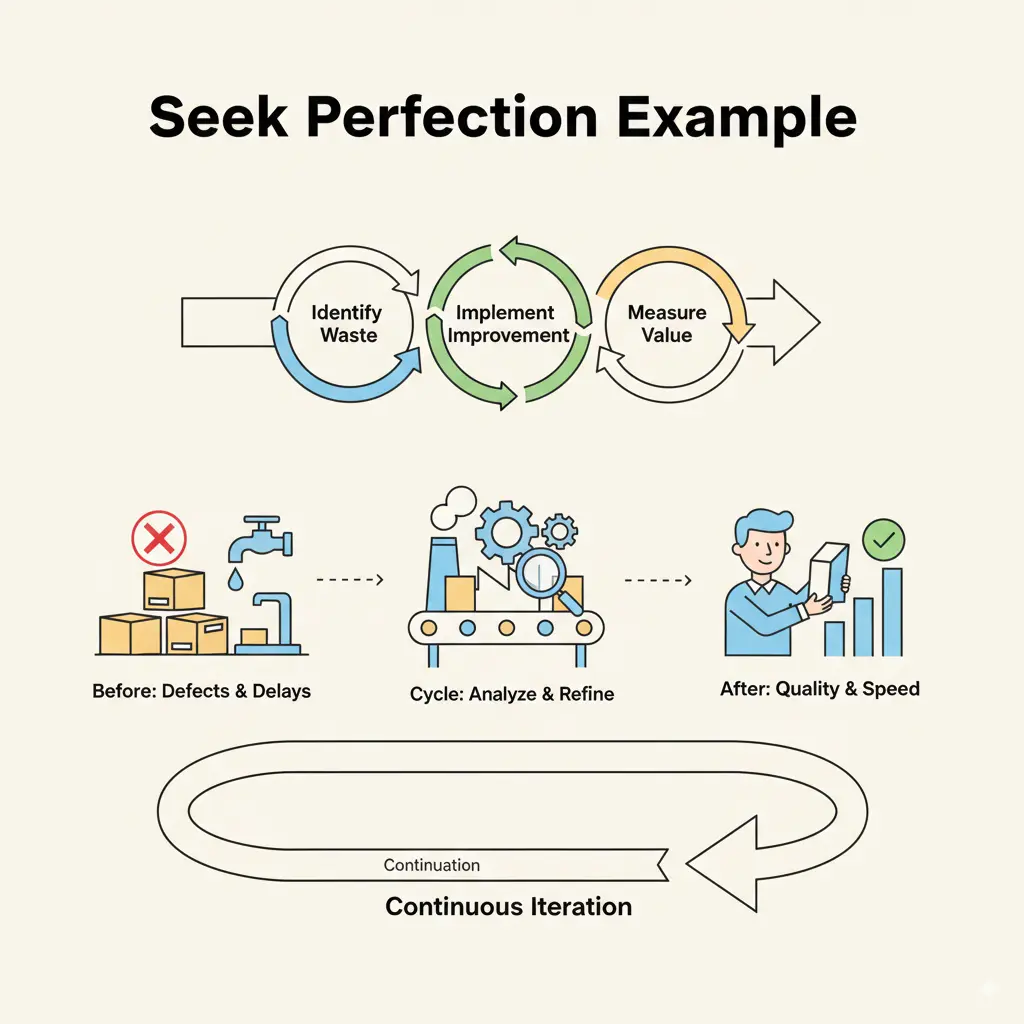
Principle 5: Seek Perfection
Lean is not just a one-time solution for businesses and managers but a mindset driven by continuous improvement. The goal of lean is not to reach a perfect stage, it is to keep striving for higher quality levels and efficiency. The concept of continuous improvement (kaizen) in lean ensures processes are regularly reviewed, waste is properly eliminated and the whole organization commits to achieve high quality and efficiency level, which are key business improvement techniques.
Checklist for Seeking Perfection
Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
Encourage employees at all level to suggest continuous improvements across the processes and pursue lean certification for mastery.
Reward employees for bringing small changes and major innovation.
5S methodology
Ensure the implementation of 5S cyclic methodology of lean i.e. sort, set in order, shine, standardize and sustain this leads to continuous improvement.
Ensure the workplace is always ready for improvement.
Standardization of Practices
Set and define best method for each process and introduce a standard base line for further improvement.
Consistently Eliminate Waste
Ensure that all the 8 types of waste are regularly monitored and eliminated across the processes.
Focus on the customers values
Take regular feedback from the customers to align their values with the business process as well as to guide improvements.
Build long-term thinking
Avoid short-term and quick solutions to the challenges.
Ensure employees are trained enough to make sustainable and effective decisions that leads to long-term benefit and improvement.
Why it matters: Seeking perfection really matters in lean thinking as the first four principles eliminate waste and increases efficiency. This principle is the most crucial aspect of lean as makes continuous improvement part of an organization keeping the business adaptable. It ensures that improvement is not short-term but becomes part of the organization culture. This principle embeds a culture of continuous learning and innovation leading to long-term competitive advantage.
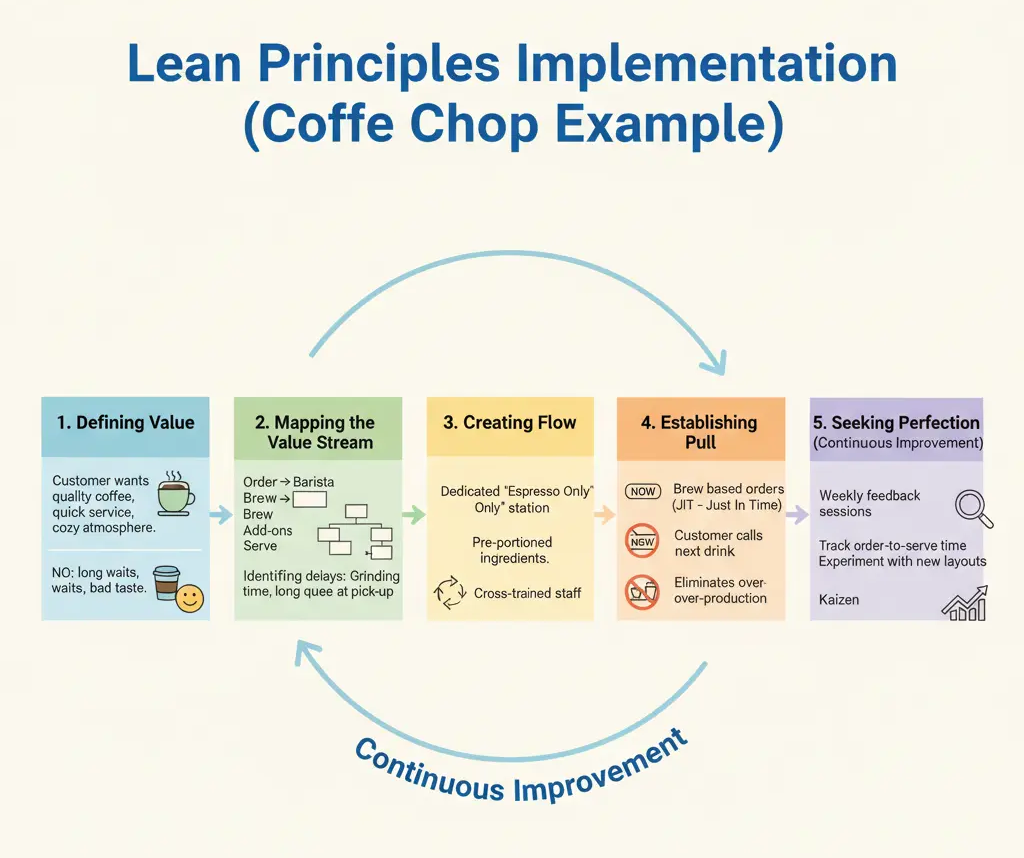
Implementation of Five Lean Principles
Each principle of lean provides its own value and benefit but, the true effectiveness of lean emerges when they are applied as an interconnected system.
Businesses, managers and students should think of these principles as a continuous cycle of improvement rather than separate steps to tick off. Each principle of lean feeds into the next principle creating an integrated system for increasing efficiencies and eliminating waste.
Defining value provide businesses with a direction, while mapping the value stream exposes inefficiencies. Creating flow ensure smooth movement of processes, and establishing pull eliminates over-production. Seeking perfection drives continuous improvement within the organization leading to long-term progress.
By applying these five principles, Toyota not only reduced waste and improved efficiency but also became a leader in the automotive industry, known for reliable and cost effective vehicles. The TPS became a global standard, with many other companies across various industries adopting Lean principles.
Importance of Integration
Integration creates a combined effect but disconnection creates blind spots. Integration is the key to lean effectiveness, as when applied in isolation, these principles may not deliver desired results. For example, if a business creates flow and establishes pull but fails to seek perfection, the transformation won’t be sustained.
Businesses often do not struggle with understanding the principle of lean but face significant challenges in integrating them together across the organization.
Common Principles Integration Challenges
Inadequate Training of Employees
The application of lean principles includes the implementation of various tools and techniques. The inadequate knowledge of employees regarding these tools can be a crucial challenge for businesses. Heavily invest in the training of employees and their skills are importance for enhancing the impact of lean.
Resistance to Change
The management and employees may show resistance to change as they may find it difficult to alter the current workflow. Provide clear direction to the employees. Inform them about the benefits of lean and the importance of their role in this transformation.
Lack of Leadership Commitment
Lean is a process of continuous improvements and requires strong leadership commitment for long-terms continuity. As, without the commitment of leadership the integration will be ineffective. Understand that lean is a long-term commitment to ensure continuous improvement, and supportive leadership is the key aspect of this integration.
Conclusion
Now it’s your time to begin your lean journey, take small steps, define value, map out the processes and establish the impact. Each step in the lean is a step towards long-term effectiveness and high efficiency. The sooner you learn it, the sooner you can unlock your potential for a successful career or an organization.