Spis treści
Introduction: What Is the 5S Methodology?
The 5S methodology—a cornerstone of lean manufacturing and the Toyota Production System—is a structured approach to eliminating waste within the broader lean management system, enhancing workplace efficiency, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By clearly defining 5S, organizations across diverse industries can reduce waste and improve workplace organization, transforming cluttered floors and desks into highly organized environments that address various forms of waste and drive productivity, safety, and quality.
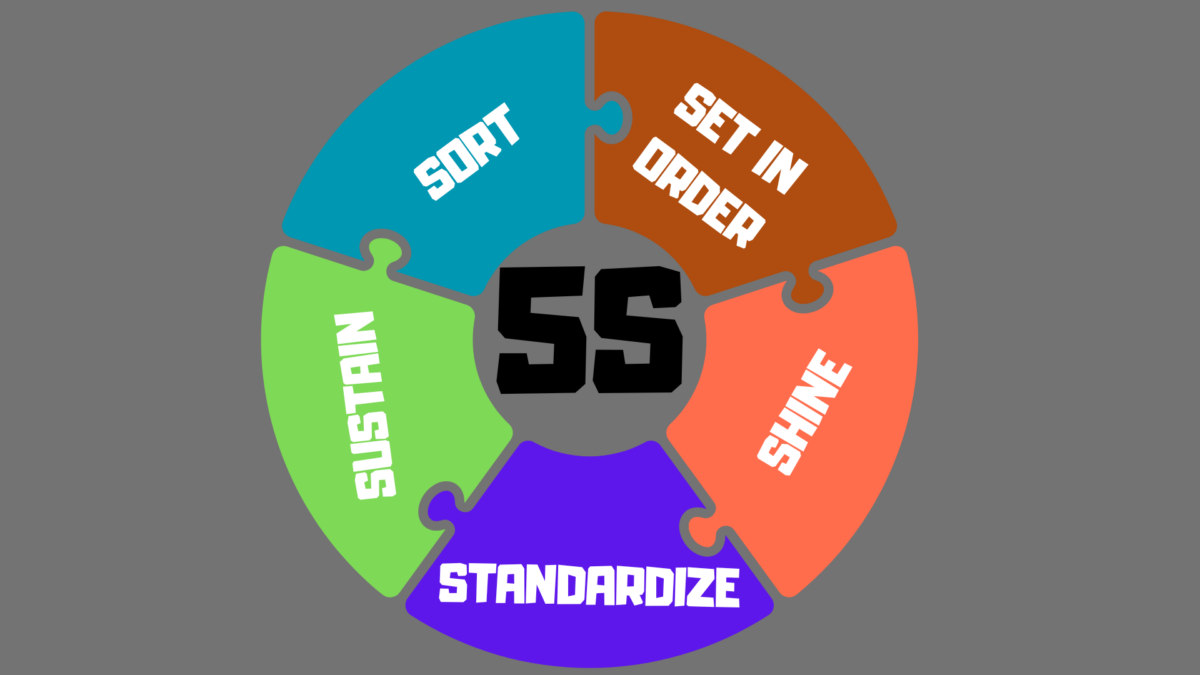
5S derives its name from five Japanese words, each representing a key principle:
- Seiri (Sort)
- Seiton (Set in Order)
- Seiso (Shine)
- Seiketsu (Standardize)
- Shitsuke (Sustain)
These steps form a five-step process to create a visual workplace where every tool, material, and instruction is clear at a glance.
Start mastering 5S today: Explore our Fundamentals of 5S Course for practical templates, real-world examples, and expert coaching.
History and Origins of 5S
The 5S methodology originated with the Toyota Production System, developed by Toyota Motor Company in Japan. The name “5S” comes from five Japanese words—Seiri, Seiton, Seiso, Seiketsu, and Shitsuke—which translate to Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. These five Japanese words form the foundation of a system designed to promote continuous improvement, minimize waste, and cultivate a highly efficient work environment. Initially focused on the manufacturing industry, 5S quickly proved its value across healthcare and office settings, as organizations recognized its ability to drive lean manufacturing principles and enhance workplace efficiency. By embedding the principles of Shine, Standardize, and Sustain into daily routines, companies worldwide have adopted 5S as a key component of their process development and ongoing improvement strategies.
1. Sort: Clearing Clutter to Reduce Waste
Definition and Objectives
Sort (Seiri) involves categorizing all items in the work environment into two categories: “needed” and “not needed.” The goal is to remove obstacles that impede flow and hide potential hazards.
Key Actions
- Conduct a sorting process (often via a Red‐Tag event) to identify items for disposal, storage, or relocation.
- Tag each item with a colored label or tag indicating its fate.
- Document decisions to inform future process development and purchasing.
Benefits
- Dramatic reduction in wasted time searching for tools and materials
- Enhanced visibility of potential hazards and equipment failure points
- Clear floor space to optimize production processes
2. Set in Order: Creating a True Visual Workplace
Definition and Objectives
Set in Order (Seiton) organizes the remaining items so that every tool, component, and supply has a designated, easily accessible location.
Key Actions
- Layout workstations using shadow boards, visual cues, and floor markings.
- Group related materials and label storage with clear icons or color codes.
- Ensure the right tools are within arm’s reach to minimize excess motion.
Optimize layouts with advanced techniques in our Advanced 5S Implementation workshop.
Benefits
- Up to 60% reduction in unnecessary movement
- Faster setup and changeover times on the manufacturing floor
- Streamlined workflows that support lean production
3. Shine: Maintaining Cleanliness and Quality
Definition and Objectives
Shine (Seiso) combines basic cleaning with inspections to maintain a clean, safe, and hazard-free workplace.
Key Actions
- Implement daily cleaning tasks, including wiping down machinery, sweeping floors, and inspecting for leaks or wear.
- Empower teams to document issues immediately via visual management boards or digital logs.
- Integrate Shine with routine maintenance schedules.
Practice Shine drills in our interactive 5S Simulation Game.
Benefits
- Early detection of defects prevents costly downtime
- Improved safety and reduced risk of workplace accidents
- Enhanced employee morale and well-being through a pleasant environment
4. Standardize: Embedding Best Practices
Definition and Objectives
Standardize (Seiketsu) codifies the first three steps—Sort, Set in Order, Shine—into standard procedures that all teams follow.
Key Actions
- Develop work instructions, SOPs, and audit checklists at each station.
- Utilize visual communication tools—such as charts, boards, and signs—to effectively display standards and metrics.
- Integrate 5S training into new-employee onboarding.
Benefits
- Consistent application of 5S across multiple departments
- Simplified training and faster ramp-up for new team members
- Foundation for other lean tools, such as Value Stream Mapping and Kanban
5. Sustain: Cultivating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Definition and Objectives
Sustain (Shitsuke) transforms 5S from a project into an intrinsic habit within the company culture.
Key Actions
- Conduct regular audits using standardized scorecards and involve all levels of the management team.
- Recognize and reward teams for 5S excellence to build employee engagement and buy-in.
- Link 5S performance to performance reviews and continuous improvement initiatives.
Benefits
- Long-term gains in operational excellence and workplace efficiency
- Continuous identification of further improvements and quick resolution of issues
- A safe environment where 5S underpins everyday work
The Role of Leadership in 5S
Strong leadership is essential for embedding the 5S methodology into an organization’s culture. When management teams actively champion 5S, they establish a tone of continuous improvement and visual management throughout the work environment. Leaders must provide clear direction, allocate resources, and ensure that training is available so every employee understands the value of 5S. By modeling best practices and recognizing team achievements, leaders help build a culture that prioritizes ongoing improvement and fosters a clean, organized workplace. This commitment from the top encourages employee engagement and ensures that 5S becomes an integral part of the organization’s culture rather than a one-time project.
Employee Engagement and Participation
The success of 5S relies heavily on employee engagement and active participation. When employees are empowered to identify unnecessary items, reduce waste, and improve workplace efficiency, they take greater ownership of their work environment. Regular training sessions, open communication, and performance reviews that highlight 5S achievements all help to foster a sense of teamwork and pride. Recognition programs and opportunities for input encourage employees to contribute ideas for continuous improvement, supporting both lean manufacturing goals and a positive workplace culture. By involving the entire team, organizations can effectively implement and sustain the 5S methodology, fully realizing its benefits.
Overcoming Challenges and Obstacles
Implementing the 5S methodology can present challenges, especially in environments where disorganization or inefficiency has become the norm. Common obstacles include resistance to change, limited resources, and the difficulty of maintaining momentum over time. To overcome these hurdles, organizations should focus on creating a visual workplace using tools such as shadow boards and visual cues, which help identify potential hazards and reduce waste. Proactively addressing equipment failures and safety hazards, and providing ongoing support and training, helps teams work more efficiently and safely. By staying committed to the 5S process and regularly reinforcing its principles, organizations can transform obstacles into opportunities for workplace efficiency and improvement.
Integrating 5S with Other Lean Tools
While the 5S methodology stands on its own, pairing it with complementary lean practices amplifies results. Integrating 5S with other lean tools is highly effective for reducing waste and helps optimize productivity across the organization:
- Value Stream Mapping: Pinpoints waste areas for 5S focus.
- Pull Systems (Kanban): Uses 5S-organized cells as clear pull points.
- PDCA Cycles: Embeds the five-step process into ongoing Plan-Do-Check-Act loops.
- Six Sigma Collaboration: Provides data-driven insights to refine and standardize processes.
Case Study: Automotive Industry Application
A leading auto manufacturer applied the 5S methodology to one production line and achieved:
- 30% reduction in parts retrieval time
- 20% fewer workplace accidents due to improved hazard visibility
- 10% boost in overall throughput after two months
This classic example underscores how 5S drives real, measurable improvements.
Measuring Your 5S Success
Key performance indicators to track include:
- Search Time: Reduction in average time spent finding tools and materials
- Audit Compliance Rate: Percentage of stations meeting 5S standards
- Safety Incidents: Decrease in near-misses and accidents
- Throughput: Increase in units per labor hour
- Employee Engagement: Survey scores on workplace satisfaction
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many organizations stumble during 5S implementation by overlooking key factors that contribute to success. Failing to provide adequate training, neglecting to set clear goals, or failing to conduct regular audits can undermine the effectiveness of the 5S system. Another frequent mistake is focusing solely on cleaning rather than on creating a safe, efficient, and organized work environment. To realize the many benefits of lean manufacturing, it’s crucial to emphasize continuous improvement, supported by regular performance reviews and employee involvement. By avoiding these pitfalls and maintaining a commitment to the 5S methodology, organizations can enhance employee morale, minimize waste, and foster a culture where efficiency and safety thrive.
Why 5S Methodology Matters Across Industries
Beyond manufacturing, 5S benefits:
- Healthcare: Organize medical supplies to enhance patient safety
- Offices: Create digital and physical 5S zones for knowledge workers
- Food & Beverage: Maintain hygiene standards in kitchens and storage
- Logistics: Streamline warehouse layouts for efficient picking
Conclusion
Defining the 5S methodology is about unlocking a systematic approach to eliminating waste, boosting productivity, and embedding continuous improvement into your organization’s DNA. By rigorously applying Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain—and integrating with other lean tools—you’ll build a safer, more efficient, and more engaging visual workplace.
👉 Ready to transform? Enroll now in our Fundamentals of 5S Course for a comprehensive pathway to a world-class visual workplace!