Spis treści
Lean in Production: Process Improvement for Eliminating Waste and Maximizing Efficiency
Lean process improvement eliminates waste, maximizes efficiency, and delivers greater customer value. Rooted in the Toyota Production System (TPS), lean thinking has transformed industries by emphasizing customer needs, optimizing workflows, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. The Toyota Production System (TPS) was developed by Toyota Motor Corporation in the automotive industry after World War II, drawing on earlier approaches such as scientific management. Lean manufacturing was later coined to describe the lean production system pioneered by Toyota, which focused on reducing waste, implementing just-in-time production, and promoting continuous improvement. This historical context highlights how World War II and the automotive industry shaped modern lean practices and efficiency methodologies. In this guide, you’ll explore the core principles of lean, essential tools like 5S, and actionable strategies for implementation. Plus, we’ll highlight real-world applications and show how engaging your team is key to sustained success.
Check out the Lean Management course for a comprehensive guide to mastering lean tools and methodologies.
Understanding Lean Process Improvement
Understanding lean manufacturing is essential for modern organizations seeking to enhance operational efficiency, reduce waste, and create value for customers.
Lean process improvement focuses on identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities to streamline operations, optimize production and manufacturing processes, and improve customer satisfaction. Organizations can reduce costs, improve quality, simplify lean processes, and analyze production cycles for greater efficiency and responsiveness by optimizing processes and eliminating waste. The core idea is simple: deliver value to the customer as quickly and efficiently as possible.
One essential aspect of lean is problem-solving. Learning how to tackle root causes effectively is critical for success. For step-by-step methods, explore the Problem-Solving Process course.
Core Principles of Lean Thinking
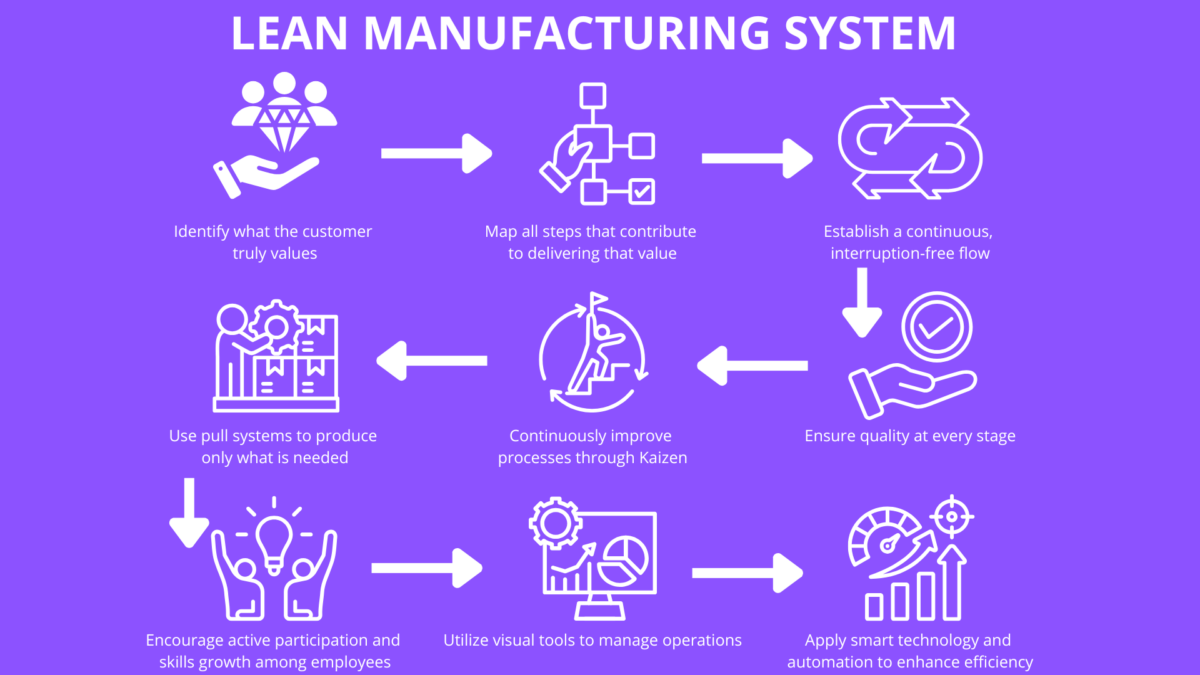
Lean thinking is built on the five key principles of lean manufacturing, which serve as the key principles for achieving efficiency, waste reduction, and continuous improvement:
- Define value from the customer’s perspective.
- Map the value stream to identify and eliminate waste.
- Create continuous flow (a core lean principle in lean manufacturing), focusing on establishing flow and removing barriers to ensure a smooth, uninterrupted process—this is essential for creating flow and optimizing efficiency.
- Establish pull based on demand.
- Pursue continuous improvement.
Applying lean principles in daily operations is crucial for sustaining improvements, reducing waste, and fostering a culture of operational excellence.
Each principle contributes to a culture where teams are empowered to drive improvements daily. If you’re interested in embedding continuous improvement into your organization’s DNA, this Continuous Improvement course offers practical strategies and tools to get started.
The Role of Waste Elimination in Lean
Eliminating wasteful practices is at the heart of lean. Organizations improve efficiency and reduce costs by focusing on value-added activities and removing unnecessary processes. Identifying waste in all forms, including excess inventory, is essential for continuous improvement and operational excellence. This approach is supported by tools such as 5S, which ensure a clean, organized, and safe workspace. For a hands-on guide to implementing 5S effectively, enroll in The Fundamentals of 5S course.
Reducing waste and achieving waste reduction are key benefits of lean manufacturing, with minimizing excess inventory a crucial aspect of this.
Lean Tools and Techniques

A successful lean transformation depends on practical lean manufacturing techniques and lean manufacturing tools, including:
- Value Stream Mapping for visualizing workflows.
- Kanban systems for managing production flow.
- 5S for workplace organization.
- WIP Limits for controlling in-progress work.
- Production tools and lean methods focusing on waste reduction and efficiency are also essential parts of the lean toolkit.
Organizations can implement lean manufacturing by selecting the strategies and tools that best suit their unique processes and goals.
Beyond tools, fostering a collaborative environment is key. Consider the Effective Teamwork and Leadership course to strengthen leadership and teamwork within your lean initiatives.
Value Stream Mapping: Visualizing and Improving Processes
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a cornerstone of lean manufacturing. It provides organizations with a clear, visual representation of every step in delivering a product or service to the customer. By mapping the flow of materials, information, and activities, VSM enables teams to see the entire value stream from end to end, making it easier to identify and eliminate waste.
The VSM process begins by understanding the customer’s needs and mapping the current state of the process. Cross-functional teams collaborate to pinpoint areas where unnecessary steps, delays, or inefficiencies occur. Once waste is identified, the team designs a future-state map to achieve continuous flow, reduce lead times, and improve quality. This future-state vision serves as the blueprint for targeted improvements.
VSM is not limited to manufacturing; it’s equally effective in healthcare, software development, and service industries. It supports the implementation of other lean tools and techniques, such as Just-in-Time (JIT) and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), by providing a holistic view of the process and highlighting opportunities for continuous improvement.
The benefits of value stream mapping are significant: organizations achieve improved efficiency, reduced lead times, higher quality, and increased customer satisfaction. By making VSM a regular part of their lean toolkit, companies foster a culture of continuous improvement and move closer to operational excellence.
Benefits of Lean Process Improvement
Lean delivers measurable benefits across industries:
- Increased operational efficiency by reducing delays and waste.
- Improved customer satisfaction through faster delivery and better quality.
- Lower operating costs by optimizing resources.
- Improved operational efficiency through streamlined processes and reduced waste.
Lean helps organizations achieve operational excellence and create wealth by minimizing waste, increasing productivity, and optimizing processes. Incremental improvements are a hallmark of lean, leading to sustained gains over time.
These results are achieved by combining lean tools, teamwork, and problem-solving skills. To learn how to analyze problems effectively, consider the Problem-Solving Process course.
Customer Satisfaction: The Heart of Lean
At the core of lean manufacturing lies a relentless focus on customer satisfaction. Every lean initiative begins by understanding the customer’s perspective—what they value and expect, and how their needs can be met. Lean manufacturing principles guide organizations to design processes that deliver only what the customer wants, when they want it, and in the exact quantity required, creating a proper pull system.
This customer-centric approach drives every decision, from streamlining production lines to reducing lead times and improving quality. Lean organizations use metrics such as customer surveys, feedback, and retention rates to measure satisfaction and identify areas for improvement. By actively listening to customer demands and responding with agility, companies can deliver higher-quality products and services at lower costs.
Prioritizing customer satisfaction helps achieve operational excellence and creates a sustainable competitive advantage. In lean manufacturing, customer satisfaction is more than a goal—it’s a key performance indicator that shapes strategy, drives continuous improvement, and ensures long-term success.
Steps to Implement Lean Process Improvement
Implementing lean manufacturing requires a structured approach that focuses on applying lean principles to eliminate waste and enhance efficiency:
- Identify Improvement Opportunities: Analyze workflows and customer feedback.
- Develop and Test Solutions: Use root cause analysis, brainstorming, and pilot projects.
- Monitor and Standardize: Apply control charts and checklists to sustain results, emphasizing effective production scheduling to support just-in-time operations.
Unlike traditional manufacturing resource planning (MRP II) systems, which rely on forecast-driven, planning-based approaches, lean manufacturing and applying lean principles prioritize pull-based systems and continuous improvement.
A culture of continuous improvement is essential to maintaining momentum. The Continuous Improvement course provides actionable steps on embedding continuous improvement.
Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Sustainable lean transformations require a strong culture that values feedback, collaboration, and learning. Teams that share ownership of processes and feel empowered to make changes are more likely to succeed. Lean manufacturing plants benefit significantly from a high-performance supplier network and efficient processes, which drive higher productivity and quality. Building a culture of continuous improvement supports the development of efficient processes throughout the organization. Strengthen your team’s ability to lead change with the Effective Teamwork and Leadership course.
Engaging employees in the 5S methodology is a great way to start. Explore the Fundamentals of 5S course to learn how to involve your team.
Real-World Applications of Lean Process Improvement
Lean principles have been successfully applied across diverse industries:
- Lean optimizes the manufacturing system by improving material flow, reducing defects, and enhancing production quality. Lean manufacturing systems focus on streamlining the production line and refining production processes to eliminate waste and increase efficiency. Managing raw materials and inventory is essential to minimizing resource consumption and supporting sustainable practices. Optimizing manufacturing processes also involves coordinating the supply chain to enable just-in-time delivery and ensure production aligns with customer demand.
- In healthcare, lean streamlines patient flow and reduces wait times.
- In services, lean enhances customer interactions and operational performance.
Regardless of the industry, learning to manage lean initiatives is critical. The Lean Management course equips professionals with the practical skills to lead lean transformations.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Resistance to change is a frequent obstacle in lean transformations. Additionally, there is no standard lean production model; organizations must adapt lean principles to their unique challenges, as lean is more of a culture than a fixed framework. To overcome these issues, leaders must communicate the benefits, involve employees, and provide the necessary training. Tools like the Problem-Solving Process course can equip teams with methods to tackle challenges as they arise.
Maintaining momentum is another challenge. Embedding a culture of continuous improvement requires discipline, structure, and a commitment to learning. For long-term success, consider combining the Continuous Improvement course with team development resources, such as the Teamwork and Leadership course.
The Future of Lean Process Improvement
A commitment to operational excellence and a culture of continuous improvement define the future of lean process improvement. As lean manufacturing evolves, organizations increasingly leverage tools like value stream mapping and visual management to identify and eliminate waste, optimize processes, and respond swiftly to changing customer demands.
Emerging technologies, including automation and artificial intelligence, will enhance lean production systems. These innovations will help organizations accurately forecast demand, streamline supply chains, and reduce waste throughout the value stream.
Agility and adaptability will be essential as markets and customer expectations shift. Lean manufacturing organizations must remain focused on customer satisfaction, using data and metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of their lean initiatives and drive ongoing improvements.
Building a culture of continuous improvement will require active employee engagement at all levels. Organizations can achieve operational excellence and secure a competitive edge by fostering collaboration, encouraging new ideas, and relentlessly focusing on eliminating waste.
The journey toward lean excellence is ongoing. By prioritizing customer needs, embracing innovation, and committing to continuous improvement, organizations can optimize processes, deliver greater value, and thrive in an ever-changing business landscape.
Final Thoughts: Start Your Lean Journey Today
Lean process improvement is more than a methodology—a mindset that continually drives organizations to seek better working methods. Organizations can achieve operational excellence by mastering tools like 5S, building strong teams, applying effective problem-solving techniques, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
🎓 Ready to elevate your lean capabilities? Explore the full range of practical courses available at Sabat Consulting:
- Lean Management course
- Problem-Solving Process course
- The Fundamentals of 5S
- Continuous Improvement course
- Effective Teamwork and Leadership course
For an interactive experience, try the GET LEAN Simulation Game—a dynamic way to reinforce learning through real-world scenarios.
Start your lean journey today and unlock your organization’s full potential!