Mastering Lean Concepts: Essential Practices for Efficiency
Want to streamline your operations and boost efficiency? Lean concepts provide the tools to eliminate waste and maximize value. This article will explore key lean principles and techniques to help you achieve these goals.
Key Takeaways
- Lean concepts prioritize maximizing customer value and minimizing waste through continuous improvement and efficient process management.
- Key Lean methodologies, such as kaizen and value stream mapping, focus on team collaboration and visualizing processes to identify and eliminate inefficiencies.
- Implementing Lean practices can lead to significant benefits, such as cost reduction and improved productivity, though organizations may face challenges such as employee resistance and adapting to new practices.
Understanding Lean Concepts
The essence of Lean thinking is to eliminate inefficiencies and foster a culture of continuous improvement. At its core, Lean concepts focus on maximizing customer value while minimizing waste. This dual focus enhances operational efficiency and ensures that the end product or service delivered to the customer is of the highest possible value.
Defining customer value is the cornerstone of Lean methodologies. It revolves around understanding what customers are willing to pay for and ensuring that every process within the organization contributes to delivering that value. Lean management promotes continuous improvement and must align with customer demand and expectations to be genuinely effective.
The Toyota Production System (TPS) is the foundation for effective Lean manufacturing practices. TPS has set a global benchmark by focusing on waste elimination. A value stream encompasses all an organization’s actions to deliver a product or service, emphasizing value addition at each step. The primary goal of Lean philosophy is to optimize processes, minimize waste, and maximize customer value.
Want to understand the foundations of Lean? Start with the Lean Manufacturing Essentials Course.
Key Lean Principles for Success
Lean principles are built around the fundamental concept of identifying value from the customer’s perspective. Organizations can discover what customers find valuable through various methods, such as:
- Interviews
- Surveys
- Data analytics: Understanding customer needs is vital to uncover what they want delivered. This focus on customer value drives all subsequent Lean initiatives.
The kaizen methodology is a cornerstone of Lean practices, promoting team collaboration across different levels to tackle issues and improve processes. The five whys technique, an analytical tool used in kaizen, is instrumental in uncovering the root causes of problems. Continually asking “why” until the root cause is found allows organizations to implement solutions that address the real issues, not just the symptoms.
Creating flow involves ensuring that value-adding activities occur without interruptions or delays. This can be achieved by implementing pull systems and takt times to address bottlenecks. Continuous flow in Lean manufacturing refers to the smooth movement of work-in-progress with minimal buffers, eliminating waste such as inventory, waiting time, and transport. The ultimate goal is to create a culture of constant improvement that ensures long-term success.
Value Stream Mapping Explained
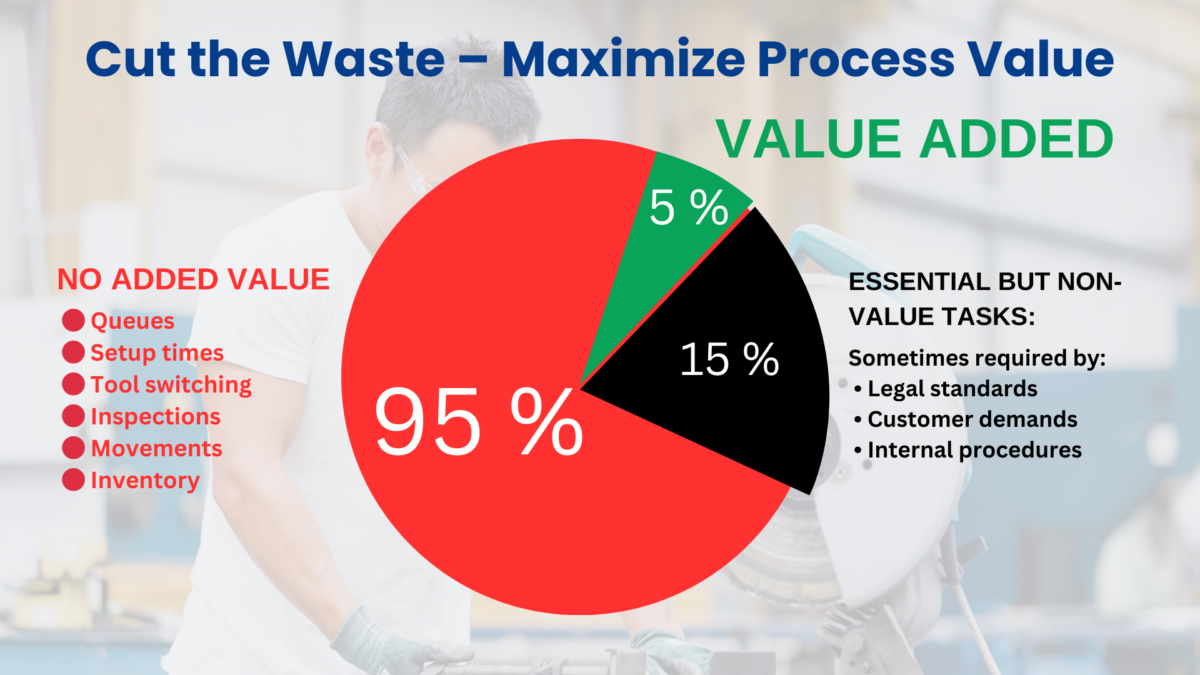
Value stream mapping is a powerful tool for visually mapping the production flow within an organization. It helps us use the customer’s value as a reference to identify all activities contributing to that value. Mapping the value stream allows organizations to identify value-adding activities and pinpoint waste.
Identifying and mapping the value stream allows organizations to pinpoint optimization opportunities like bottlenecks and wastes. This value stream analysis is pivotal in understanding the entire process design flow, not just individual tasks. Consequently, strategies can be developed to ensure a smooth flow of value-adding activities, such as breaking down steps, reconfiguring production processes, and training employees.
Value stream mapping is also utilized in the kaizen methodology to visualize processes and identify non-value-adding elements, aiding in targeted waste elimination. Exposing waste through value stream mapping provides a roadmap for improvement, ensuring that the remaining steps flow smoothly without interruptions.
The Role of Kaizen in Lean Practices
Kaizen, a strategy for regular incremental improvements, plays a crucial role in Lean practices. It involves the collective talent of employees to improve work processes continuously. Kaizen methods include continuous improvement and the PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act) cycle, which guides organizations through change.
The pursuit of perfection in a Lean organization involves continuous efforts from all employees to improve processes based on customer needs. This collective effort helps eliminate waste and fosters a culture of constant improvement. Employee involvement in Lean initiatives can significantly enhance morale and promote a positive work environment.
Leaders play a crucial role in establishing a culture of respect, which should be maintained throughout the organization. This culture of respect and continuous improvement influences organizational culture and integrates Lean thinking into everyday practices.
Companies like Intel apply lean methods and Lean principles in their production processes, focusing on minimizing inventory and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Improve your production systems by enrolling in the Lean Management Fundamentals.
Implementing the 5S Method
The 5S method is a cornerstone of Lean practices. It aims to enhance workplace efficiency by maintaining an orderly environment through organizing, cleaning, and visual management. The first step, Sort, involves removing unnecessary items from the workspace, often using a technique known as ‘red tagging’ to identify what is not essential.
Set in Order focuses on creating effective storage solutions, ensuring that tools and materials are easily accessible and identifiable. The Shine step emphasizes regular cleaning of the workspace to ensure workers can identify any equipment issues that may require maintenance, keeping the environment focused. These solutions come in various forms to meet different needs.
Standardization establishes consistent practice within the workspace to maintain the organization that was achieved through the previous steps. The final step, Sustain, is crucial as it focuses on ingraining the 5S practices into the organization’s culture to maintain improvements over time.
Consistent application of the 5S method significantly enhances workplace efficiency and problem-solving capabilities.
Kanban for Smooth Workflow
Kanban, a method originating from the Toyota Production System, is designed to regulate the flow of goods using visual signal cards. This pull system enhances productivity by visualizing work in progress and allowing teams to manage tasks based on actual demand, thereby minimizing inventory. WIP (Work In Progress) limits in Kanban ensure that work does not exceed a set number, helping to maintain a steady flow and reduce delays.
Kanban boards serve as visual aids that depict the status of tasks, enabling teams to track progress and identify bottlenecks instantly. This visual management system promotes continuous improvement by encouraging immediate resolutions to problems as they arise in the workflow.
Applying Lean principles through Kanban helps organizations achieve a smoother production flow, reduce waiting time, and boost productivity in less time.
The Importance of Respect for People
Respect for People is the cornerstone of Lean principles, emphasizing the value of every individual’s input within a team. Employees’ motivation and morale increase when they feel valued, leading to higher productivity. An environment that fosters mutual respect enhances communication, collaboration, and, ultimately, project outcomes based on the principle of respect.
Transparency and trust among team members are significantly improved when respect is prioritized in the workplace. Listening to diverse perspectives within a team contributes to better decision-making and innovation. Team members’ willingness to embrace conflict constructively is essential for maintaining a healthy Lean workplace culture.
Creating a culture of respect and support ensures long-term success and continuous improvement.
Standard Lean Tools and Techniques
Learning tools and techniques is essential for implementing Lean principles effectively. Value stream mapping is one such tool, which involves visualizing all components necessary for delivering a product or service. This facilitates more transparent communication and collaboration among team members. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is another framework for measuring manufacturing process productivity loss.
Muda, which refers to any activity in the production process that does not add value to the final product, is a key concept in Lean. Tools include:
- Poka-Yoke: prevents defects in production
- Jidoka: provides partial automation that stops when defects are detected
- Andon: serves as a real-time communication tool for immediate problem identification within the production process, contributing to waste reduction.
Continuous Flow aims to allow work-in-progress to move smoothly through production with minimal interruptions. At the same time, Standardized Work captures best practices in documented procedures to reduce variability and improve efficiency. Techniques like Single-Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) focus on minimizing changeover times to enable more flexible production. Bottleneck Analysis helps identify limits on overall throughput, improve production processes, and prevent over-processing.
Discover how Lean Manufacturing principles can transform your business in the Lean Strategy Training.
Benefits and Challenges of Lean Implementation
Organizations that adopt Lean practices often experience significant benefits, including an average reduction of 15% in overall cost. However, implementing Lean is not without challenges. Potential drawbacks include employee resistance and initial costs associated with training and technology. Forty percent of businesses encounter employee resistance as a significant barrier during Lean implementation.
Challenges and essential factors in Lean implementation include:
- A lack of flexibility can hinder scalability, with 20% of companies facing issues when expanding these practices.
- Higher employee workloads during Lean implementation can lead to perceptions of increased stress, complicating the transition.
- Clear communication is vital during Lean implementation to avoid misunderstandings and a smooth transition.
Despite these challenges, the long-term benefits of Lean, such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved employee involvement, make it a worthwhile endeavor for organizations striving for continuous improvement.
Real-World Applications of Lean
Lean principles originated from the Toyota Production System and have since evolved to influence various sectors. The value stream mapping technique, for instance, originated from Toyota. It focuses on the overall process flow rather than individual tasks. Real-world applications of value stream mapping have demonstrated significant time savings and improved collaboration in various organizations.
Companies like Amazon utilize the Pick-to-Belt method to streamline their fulfillment centers, enhancing efficiency by reducing unnecessary movements during the packing process. Nike’s lean strategy includes maintaining minimal inventory levels, which helps cut costs and prevent products from becoming outdated.
Caterpillar Inc. has developed its production system inspired by Toyota, focusing on streamlining project processes to eliminate waste that has been eliminated. John Deere invested substantially in Lean manufacturing to enhance operations by removing non-value-adding activities, boosting overall productivity, and developing overall efficiency.
General Electric has adopted Lean practices across its divisions, significantly reducing production time and inventory levels. Parker Hannifin integrates advanced electronic strategies into its Lean manufacturing approach, focusing on efficiency and waste elimination. These real-world examples highlight the versatility and effectiveness of Lean principles in various industries.
Summary
In summary, mastering Lean concepts involves understanding and applying fundamental principles such as maximizing customer value and minimizing waste. Tools like value stream mapping, the 5S method, and Kanban are essential for visualizing and optimizing processes. The kaizen methodology and respect for people are crucial for fostering a culture of continuous improvement and employee engagement.
By adopting Lean principles, organizations can achieve significant benefits, including cost reduction, increased efficiency, and improved employee morale. While challenges exist, such as initial costs and employee resistance, the long-term advantages make Lean a valuable strategy for any organization aiming for excellence. Embrace Lean thinking and transform your organization into a model of efficiency and effectiveness.
Looking to gain a deeper understanding of lean methods? The Lean Management course equips you with everything you need to implement lean principles effectively.
Watch a free lesson from our Lean Manufacturing principles course.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of Lean philosophy?
The primary goal of Lean philosophy is to optimize processes while minimizing waste to enhance customer value. This approach ultimately leads to greater efficiency and satisfaction.
How does value stream mapping benefit an organization?
Value stream mapping significantly benefits an organization by identifying value-adding and wasteful activities. This allows for targeted process improvements and waste reduction, enhancing efficiency and productivity within the organization.
What is the role of kaizen in Lean practices?
Kaizen is crucial in Lean practices, emphasizing continuous incremental improvements through employee collaboration. This approach effectively eliminates waste and enhances processes. This ongoing commitment to improvement fosters a productive and efficient work environment.
What are the steps involved in the 5S method?
The 5S method consists of five key steps: Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. These steps collectively aim to improve workplace efficiency and organization. Implementing these steps can significantly enhance productivity and maintain a clean work environment.
What challenges might an organization face when implementing Lean?
Organizations often encounter employee resistance, high initial training and technology costs, and increased workloads during the transition to Lean. Addressing these challenges is crucial for successful implementation.
