Lean Management Principles: A Comprehensive Guide to Driving Efficiency and Value
Introduction
Understanding and implementing Lean Management Principles have become essential for organizations across all industries in an era where efficiency, agility, and customer satisfaction define long-term success. The fundamental idea behind Lean is respect for people and a commitment to continuous improvement. These principles form the backbone of the lean management system, a proven methodology aimed at delivering customer value while eliminating waste—activities that do not add value from the customer’s perspective are considered waste—improving workplace efficiency, and enabling continuous improvement.
This article explores the five lean principles, which form the foundational framework for Lean methodology, the core principles of lean management, how they apply to different business functions, and how you can implement them effectively using practical tools and strategies as a manager or leader.
🎓 Want to go beyond theory? Explore our Lean Management course for a practical, experience-based approach to applying lean principles across your organization.
What Are Lean Management Principles?
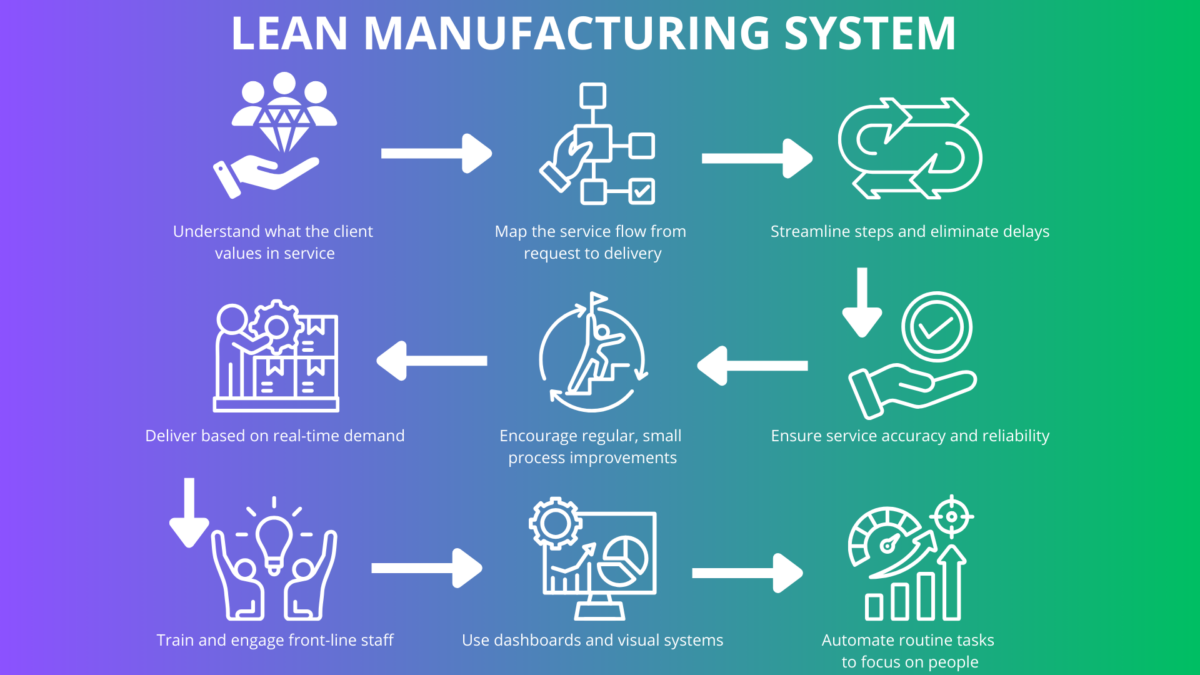
Lean Management Principles refer to a structured approach for optimizing organizational processes to deliver more value with fewer resources. Based on the Toyota Production System, Lean methodology originated in lean manufacturing and has since been adopted across industries. These principles aim to create an efficient and effective organization that continuously improves operations by identifying and removing non-value-adding activities. Lean principles provide a structured approach to continuous improvement and waste reduction.
At their core, the five lean principles form the key pillars of the Lean methodology:
- Define Value
- Map the Value Stream
- Create Flow
- Establish Pull
- Pursue Perfection
Each lean principle serves as a key pillar supporting Lean management. These principles provide a foundation for organizations to remain competitive, enhance process improvement, and deliver what customers find valuable, on time and without waste.
1. Define Value
The first principle revolves around identifying what the end customer truly values. Defining customer needs and expectations is the crucial first step in Lean, as it establishes a clear understanding of who the customer is and what they value. It requires a deep understanding of customer expectations and aligning your operations to meet actual or latent needs. By focusing on perceived value and designing processes to deliver the most value to end customers, organizations can eliminate efforts that do not directly contribute to the final product or service.
Managers should start by asking:
- What do our end customers want and need?
- What features or services are they willing to pay for?
- How can we ensure that our processes are focused on delivering those outcomes?
2. Map the Value Stream
Once value is defined, the next step is mapping the value stream, which is known as the second Lean principle—the complete set of actions (both value-adding and non-value-adding) required to bring a product or service from concept to delivery. This step helps identify pure waste and eliminate unnecessary processes to improve efficiency, as non-value-adding activities are considered waste and should be eliminated.
🧰 Learn how to perform effective value stream mapping in our Lean Management course, packed with real-world examples and exercises. The goal is to eliminate waste and improve efficiency throughout the value stream.
Common Wastes Identified:
- Overproduction
- Waiting time
- Unnecessary transportation
- Excess inventory
- Overprocessing
- Defects and rework
- Underutilized talent
3. Create Flow

After eliminating waste, it’s essential to ensure that value-adding steps occur in a tight sequence. This leads to a smooth flow of work and materials through the production process or service delivery system. A continuous workflow ensures that value-adding steps flow smoothly without interruption, reducing delays and maximizing efficiency. The goal is to avoid context switching, delays, and interruptions.
Tools that help establish flow:
- Standardized work
- Cross-functional teams
- Creating cross functional departments to break down silos and improve collaboration
- Workplace redesign
Creating flow also involves improving workplace efficiency through lean practices like 5S, visual management, and just-in-time delivery. Creating cross-functional departments supports continuous workflow and helps processes flow smoothly by integrating different skill sets and fostering collaboration across the organization.
📦 Want to bring flow into your workspace? Check out our 5S Workplace Organization course to implement structured work environments.
4. Establish Pull
A pull system means producing only what is needed, when it is needed, and in just the required quantities. This helps reduce overproduction, one of the worst forms of waste. Pull-based systems ensure that resources are allocated efficiently, responding to customer requirements rather than forecasts. A pull-based system helps limit inventory and work-in-progress by producing only what is needed, when it is needed, based on actual customer demand.
Applications of pull:
- Kanban systems
- Inventory management
- Production scheduling based on demand
- Establish pull inventory to align production with actual customer demand
Discover how pull systems improve responsiveness and reduce cost in our Lean Management course. Pull based systems are designed to limit inventory and reduce waste.
5. Pursue Perfection
The final principle encourages continuously improving all aspects of the value stream. Lean organizations become learning organizations, driven by the relentless pursuit of excellence, where team members play a crucial role in driving continuous improvement and waste reduction.
This principle supports:
- Iterative improvement cycles
- Feedback from frontline employees
- Training employees in lean methods
- Engaging team members in waste reduction initiatives
Looking to build a culture of innovation and continuous learning? Our Continuous Improvement course is your go-to resource for fostering a learning organization that supports ongoing waste reduction.
Why Are Lean Management Principles Important?
The lean management concept promotes clarity, accountability, and agility. Its principles encourage creating a lean mindset that aligns teams with organizational goals. They are critical for:
- Increasing customer satisfaction
- Improving team collaboration
- Enabling faster response to change
- Delivering significant improvements in work processes and outcomes
Implementing Lean Management Principles: A Roadmap for Leaders
Step 1: Assess Your Current State
Use tools like value stream mapping and qualitative and quantitative techniques to evaluate current processes.
Step 2: Set Clear Objectives
Tie Lean initiatives to key processes and business outcomes.
Step 3: Train and Empower Employees
Develop internal champions who understand lean principles and can apply them across departments.
Step 4: Launch Pilot Projects
Start small to test ideas, gather data, and refine strategies.
Step 5: Monitor, Measure, and Adjust
Use metrics such as lead time, quality indicators, and employee engagement to guide improvements.
Improve your leadership approach and empower your team with our Teamwork and Leadership course.
Real-World Applications of Lean Management Principles
Manufacturing
Adopted globally as a standard for production process excellence, Lean supports faster turnaround, higher quality, and reduced waste.
Healthcare
Lean supports patient-centered care by eliminating delays and improving service delivery.
Logistics and Supply Chain
Improves forecasting, inventory management, and responsiveness.
Knowledge Work
Helps reduce scope creep, over-processing, and inefficiencies in digital workflows.
Want to put Lean into practice immediately? Try our Lean Simulation Game and experience hands-on how lean management works in dynamic environments.
Common Misconceptions About Lean Management Principles
- Myth: Lean is only for manufacturing
- Reality: Lean applies to any process, from hospitals to tech startups.
- Myth: Lean is about cost-cutting
- Reality: While cost reductions are a byproduct, the primary focus is delivering more customer value.
- Myth: Lean is a one-time project
- Reality: Lean is a long-term approach centered on building a culture of improvement.
How to Sustain Lean Management Principles Over Time
- Encourage ownership at all levels
- Review processes regularly
- Share success stories to maintain motivation
- Align Lean efforts with strategic planning
🎯 Learn how to implement and sustain lean practices over time in our Lean Management course, filled with expert strategies.
Conclusion
Lean Management Principles offer a clear framework for delivering more value, reducing waste, and creating adaptable, resilient organizations. Whether you’re just starting your lean journey or looking to scale existing initiatives, these principles provide a reference point for success.
🎓 Ready to implement Lean where it counts? Join our Lean Management course and gain practical insights from over 25 years of experience implementing lean principles and 5S methodology in various industries.
👉 You can preview a lesson for free and see how applicable the material is to your daily operations.
And if you’re interested in a fun, engaging way to internalize these principles, don’t miss our Lean Simulation Game—a practical training tool designed to bring Lean to life.
Also, explore our other expert-led courses:
Mastering Lean Management Principles isn’t just good for business—it’s essential for building future-ready organizations.

