Understanding Lean Transformation
Lean transformation is a comprehensive and strategic shift in how an organization operates, with the ultimate goal of maximizing customer value while minimizing waste. Lean transformation is essential because it enables organizations to improve efficiency, competitiveness, and adaptability by eliminating waste, optimizing processes, and fostering continuous improvement, ultimately leading to increased profitability and resilience.
Rooted in the principles of the Toyota Production System, this approach redefines traditional business practices through a combination of lean thinking, leadership behaviors, and a strong focus on continuous improvement. Lean transformation offers a systematic approach to process improvement, providing a structured and methodical way to analyze and enhance organizational processes at all levels.
A successful lean transformation is not just about implementing tools—it’s about changing the organization’s culture and mindset, including challenging existing assumptions and perspectives to enable lasting change. Thought: What underlying beliefs and attitudes need to be reconsidered to embrace Lean transformation fully?
The Lean Transformation Model
At the core of a lean transformation model is a structured framework that guides organizations in identifying opportunities for improvement and executing sustainable changes. Embedding lean principles within the organization’s culture and structure is essential for long-term success. The exact process applies across different stages of the lean journey, ensuring a standardized approach to transformation. It includes several important components:
- Lean Thinking: A mindset that prioritizes customer value, efficiency, and long-term improvement.
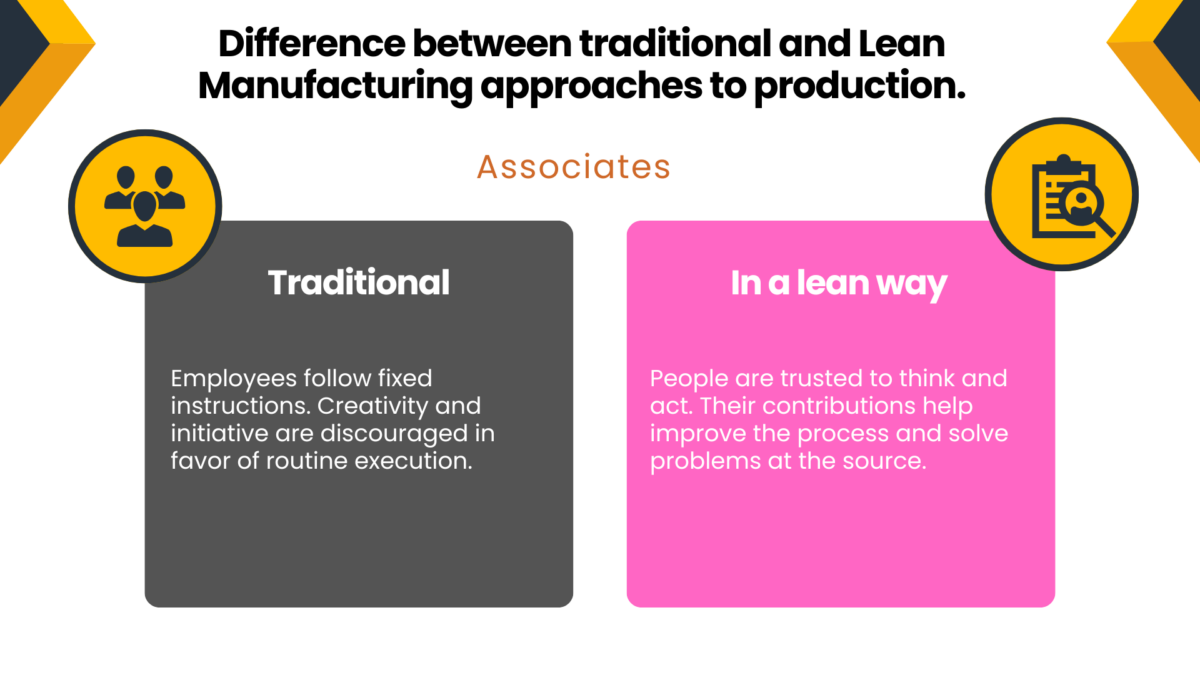
- Leadership Behaviors: Leaders must model lean values and empower teams through coaching and support. Lean transformation can begin with a single team and then scale across the organization.
- Capability Development: Building employee skills to solve problems and drive change through a continuous learning process.
- Value Stream Mapping: Analyzing workflows to eliminate waste and streamline production processes.
- Lean Management System: Establishing metrics, routines, and visual management to track progress and sustain improvements.
Lean transformation is not limited to manufacturing; it is also highly applicable to knowledge work, such as software development, marketing, and other knowledge-based activities, where optimizing processes and eliminating waste are equally important.
Why Lean Transformation Is Important
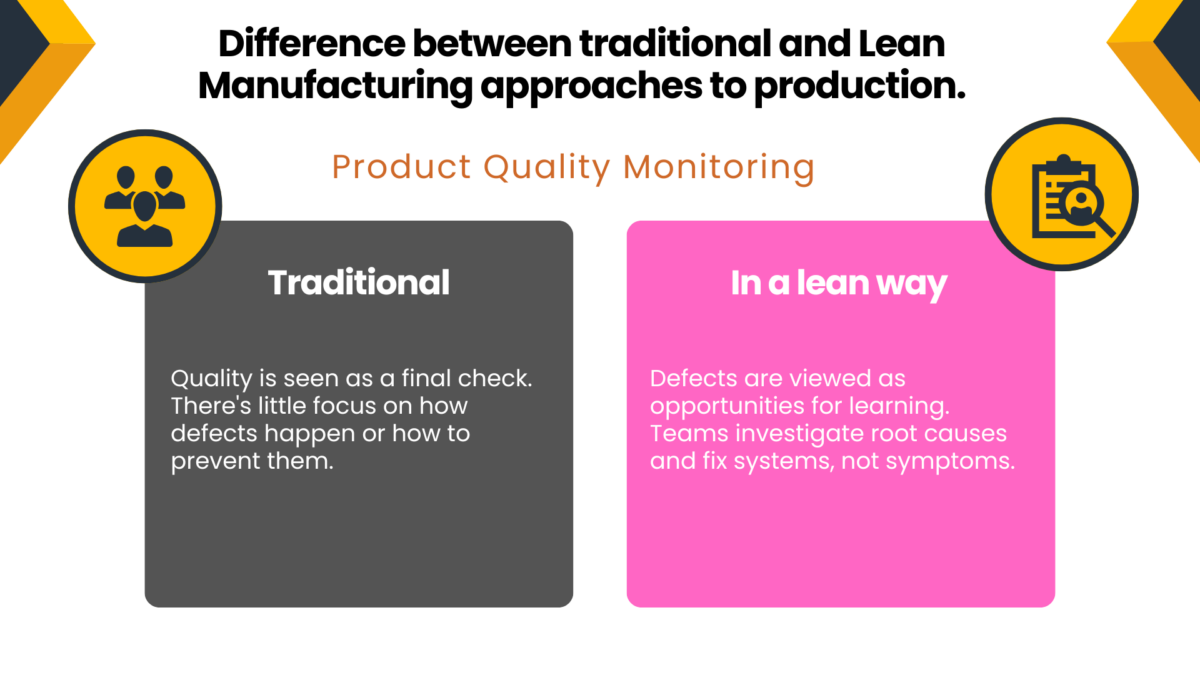
Implementing a lean transformation enables companies to achieve cost reduction, minimize waste, generate less waste, shorten lead times, lower costs, improve product quality, and focus on quality improvement—all while driving increased productivity and enhancing customer satisfaction. It also fosters a culture where continuous improvement becomes second nature and where every team member is engaged in delivering maximum value by understanding and addressing the customer’s needs, preferences, and expectations. This shift from traditional business practices to lean practices enables greater flexibility, faster decision-making, and more substantial alignment between strategic goals and daily work.
Key Elements of a Lean Transformation
Value Stream Mapping
One of the first steps in the lean transformation process is value stream mapping. This technique enables organizations to visualize their end-to-end processes, identify bottlenecks, and pinpoint areas of waste. It also allows a clearer understanding of how to create more value with fewer resources.
Lean Tools and Methods
A wide array of lean tools supports transformation efforts, including:
- 5S Workplace Organization
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement Events)
- Standard Work
- Visual Management Systems
- Pull Systems and Kanban
These tools must be applied in the context of a broader lean transformation framework, not as isolated initiatives but as part of a holistic system.
Continuous Improvement Culture
To truly transform, an organization must embrace a culture of continuous learning and improvement. The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle becomes the foundation of this approach, promoting experimentation, reflection, and adaptation at every level of the business. This requires not only process changes but also shifts in thinking, behaviors, and assumptions.
The Role of Leadership and Management
Leadership and management are the driving forces behind a successful lean transformation. Lean transformation enables companies to achieve operational excellence by embedding a culture of continuous improvement and respect for people at every level. Effective leaders must fully embrace lean thinking, focusing on delivering value to customers and systematically eliminating waste from all processes.
A key responsibility of leadership is to develop and sustain a management system that supports lean principles, such as value stream mapping and stream mapping, which help visualize and optimize the value stream. Leaders must model the right behaviors—encouraging data-driven decision-making, fostering open communication, and empowering employees to engage in problem-solving and continuous learning.
By championing lean initiatives and aligning the organization around a shared vision of improvement, leadership ensures that every team member is committed to creating value and driving transformation. This approach not only supports the adoption of lean practices but also sustains momentum for ongoing improvement, making lean transformation a lasting part of the organizational culture.
Building Lean Capability Across the Organization
Developing lean capability across the organization is essential for the successful implementation and sustainability of lean transformation. This means equipping employees at all levels with the skills, knowledge, and mindset needed to drive continuous improvement and process excellence.
Embedding lean principles into the organizational culture starts with capability development—fostering a problem-solving mindset, encouraging experimentation, and promoting shared responsibility for improvement. Leaders play a pivotal role in supporting this development by providing access to lean tools such as value stream mapping, stream mapping, and the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) cycle, which are critical for effective process improvement and waste elimination.
By investing in training, coaching, and hands-on learning, organizations empower their teams to identify opportunities for improvement, implement changes, and sustain results. This collective commitment to capability development ensures that lean transformation is not just a top-down initiative but a shared journey that engages everyone in the pursuit of value and excellence.
The Role of Basic Thinking in Lean Transformation
Basic thinking is at the heart of every successful lean transformation. It requires organizations to challenge existing assumptions and adopt a new way of thinking about value creation and waste elimination. Lean thinking is built on asking fundamental questions—such as “What problem are we trying to solve?” and “What value do we want to create for our customers?”—to guide decision-making and improvement efforts.
This thinking mindset enables organizations to look beyond surface-level fixes and address the root causes of inefficiency. By focusing on maximizing value for customers and continuously questioning existing processes, organizations can drive sustainable change and cultivate a culture of innovation.
Adopting a basic mindset involves developing the discipline to reflect on processes regularly, identify areas for improvement, and eliminate waste. This approach not only supports continuous improvement but also ensures that transformation efforts are aligned with the organization’s strategic goals and customer needs.
Lean Transformation in Action
Aligning Strategy with Execution
Lean transformations are most successful when leadership connects high-level strategic objectives with everyday operations. By aligning key performance indicators (KPIs) with lean goals, organizations ensure that every process improvement effort contributes to overarching business outcomes.
Developing the Lean Mindset
The shift to a lean culture involves changing deeply embedded thinking patterns. This includes:
- Understanding the current state and why it needs to change.
- Defining what value means to the customer.
- Eliminating activities that do not add value.
- Building problem-solving capabilities across the organization.
From Process Improvement to Systemic Change
Unlike traditional cost-cutting efforts, lean transformation is about systemic, sustainable change. It improves work processes and organizational culture simultaneously. The result is not only reduced waste but also higher employee engagement, better customer outcomes, and long-term growth.
Actual Work and Waste: Identifying and Eliminating Inefficiencies
A core objective of lean transformation is to identify and eliminate waste in all forms, ensuring that every activity adds value for the customer. Waste can manifest as excess inventory, unnecessary motion, waiting times, or defects—each representing lost opportunity and inefficiency within the value stream.
To effectively eliminate waste, organizations must first understand the actual work involved in delivering value. This is achieved through value stream mapping and other lean tools, which help visualize the entire process, pinpoint inefficiencies, and prioritize areas for improvement. By focusing on the value stream and using stream mapping techniques, teams can distinguish between value-adding activities and those that should be eliminated.
Reducing waste leads to significant operational improvements, including shorter lead times, reduced cycle times, and lower costs—all of which contribute to higher customer satisfaction. By making waste elimination a continuous priority, organizations can transform their processes, deliver better value, and achieve lasting results.
Measuring Progress on Your Lean Journey
Tracking progress is vital to sustaining momentum and ensuring the success of your lean journey. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as lead time, cycle time, and customer satisfaction allows organizations to measure the impact of their lean transformation efforts and identify areas for further improvement.
A robust lean management system supports continuous improvement by providing regular feedback, coaching, and opportunities for learning and growth. Data-driven analysis of KPIs enables organizations to make informed decisions, adjust strategies, and ensure that every improvement initiative is aligned to deliver maximum value to customers.
By consistently measuring progress and supporting teams with the right management systems, organizations can achieve sustainable change, maintain focus on their lean journey, and continue to deliver exceptional value to customers over the long term.
Lean Transformation Across Industries
Lean transformation isn’t limited to manufacturing. Its principles have been successfully applied in healthcare, software development, education, and public services. For instance, lean healthcare initiatives have significantly reduced patient wait times, improved safety, and optimized resource utilization—all through the application of lean thinking to healthcare delivery processes.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Common Pitfalls
- Treating lean tools as a one-time fix.
- Failing to involve frontline employees.
- Lack of sustained leadership commitment.
- Misalignment between departments or goals.
Solutions
- Develop a clear lean transformation roadmap.
- Create cross-functional teams to lead initiatives.
- Invest in ongoing training and coaching.
- Regularly review progress using visual performance dashboards.
Begin Your Lean Journey
Whether your organization is just starting or looking to revitalize its lean transformation, the key lies in adopting a situational approach tailored to your current processes and strategic needs. Remember, lean transformation is not a project—it’s a journey.
If you’re ready to lead change and master the tools and mindset behind operational excellence, start with practical training. Explore this comprehensive course: 👉 Lean Management – Build Efficient Organizations Through Continuous Improvement.
For a hands-on experience that puts lean principles into practice, try the interactive 👉 GET LEAN Simulation Game – a powerful way to visualize waste, streamline workflows, and empower teams to drive improvements.
Final Thoughts
Lean transformation is more than a method—it’s a new way of thinking that empowers individuals, improves performance, and aligns every part of the organization toward creating value. With the right mindset, tools, and strategy, any organization can realize the full potential of lean thinking.
Now is the time to move beyond theory. Join the lean journey and experience transformation that lasts.
➡️ Start your Lean Management course today ➡️ Discover the GET LEAN Simulation Game
