In a world where organizations must deliver more with less, understanding the principles of Lean management has become essential. The fundamental idea behind Lean is to maximize value while minimizing waste. Rooted in the Toyota Production System and originating from lean manufacturing, Lean management is a philosophy that aims to create an efficient and effective organization by maximizing customer value and minimizing waste. This lean philosophy provides a comprehensive approach to achieving efficiency and reducing waste.
Whether applied to manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, or software development, the Lean methodology provides a universal framework for improving performance through continuous improvement, value stream alignment, and team engagement.
This article examines the five lean principles as a practical framework, outlines how to apply them in practice, and explains why they remain a cornerstone of operational excellence across various industries.
What Are the Principles of Lean Management?
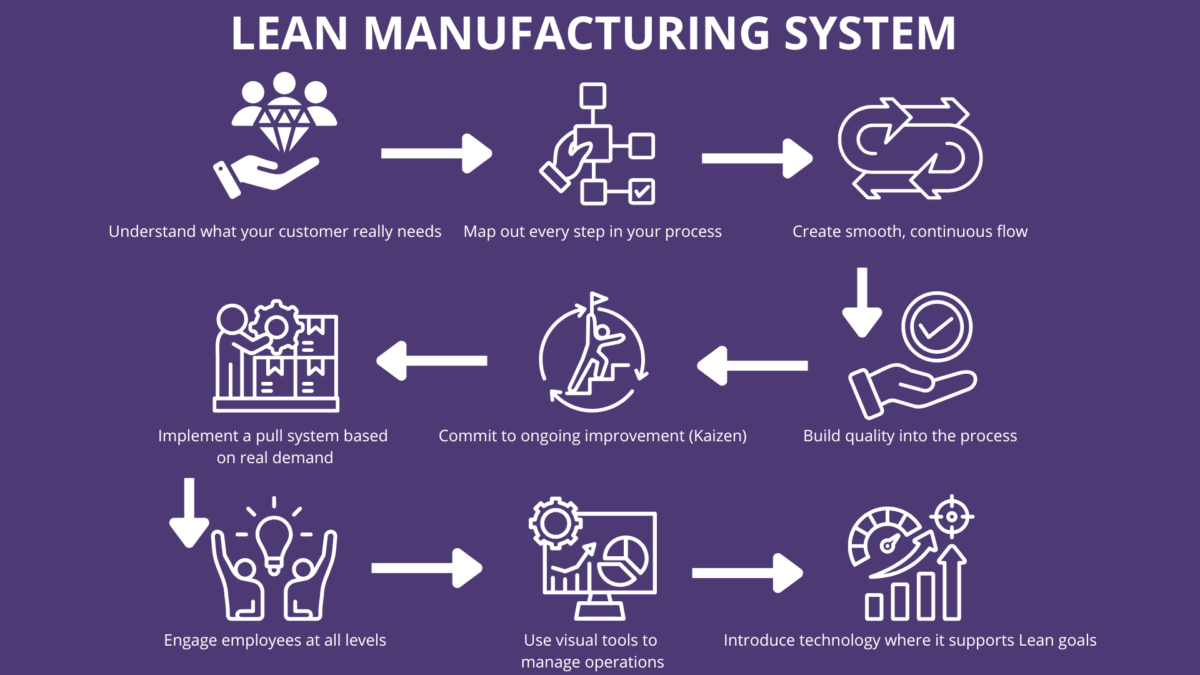
The principles of Lean management are the foundational ideas that guide the implementation of Lean. The Lean Enterprise Institute popularized these five key principles of Lean. Womack and Jones defined these principles in their influential work, providing a clear framework for Lean thinking. Lean defines value and waste through these principles, helping businesses become more agile, customer-focused, and process-driven.
Let’s break down each of the five principles of Lean and what they mean for a modern organization. These principles encourage the creation of value, flow, and continuous improvement within organizations.
1. Define Customer Value
The first Lean principle is identifying what the end customer truly values. Defining the customer is the initial step in Lean, as it ensures organizations understand who their customers are and what they perceive as valuable. This involves understanding the actual or latent needs of customers and focusing resources on activities that deliver value-added benefits.
This principle encourages organizations to:
- Use interviews, surveys, and web analytics to discover what customers find valuable
- Avoid making assumptions based on internal biases
- See value from the customer’s perspective
When companies clearly define customer value, they can better align goals and eliminate unnecessary processes that do not contribute to customer outcomes.
2. Map the Value Stream
The second Lean principle is mapping the value stream—visualizing every step in the production process or business process that contributes to delivering a product or service.
Using tools like value stream mapping, organizations can:
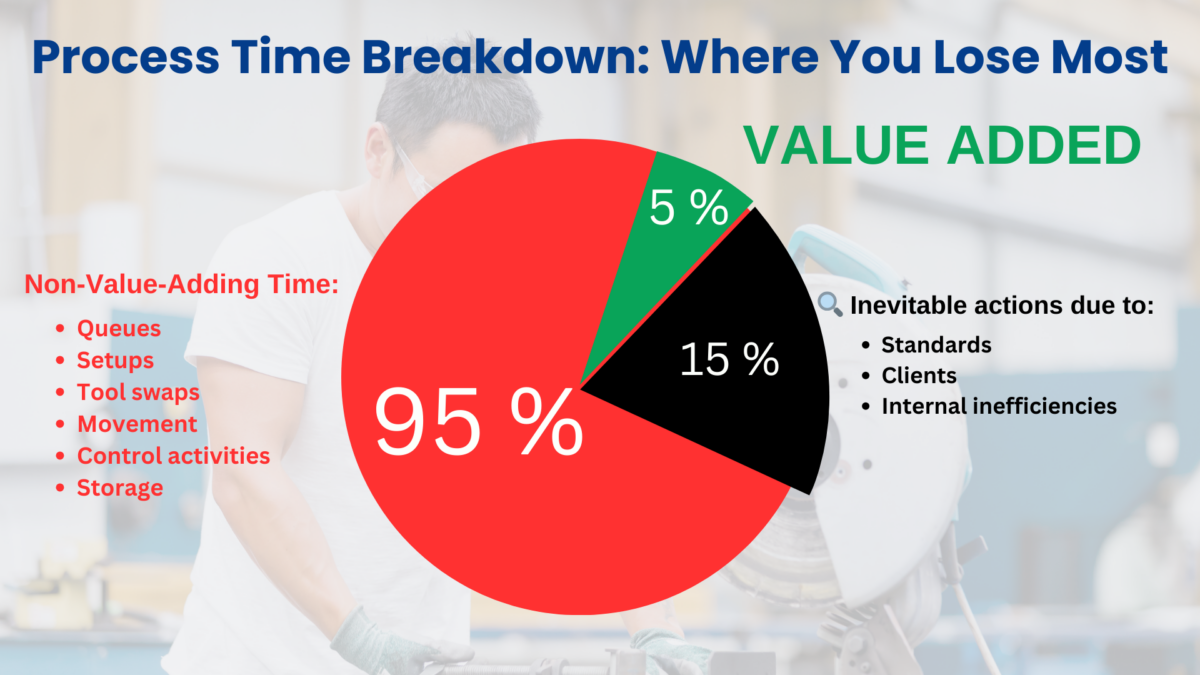
- Identify steps that are considered waste because they do not add value, as well as pure waste, and other non-value-adding steps
- Eliminate delays and redundancies
- Build a shared understanding of the entire process
By visualizing the entire value stream, teams gain clarity and can focus on eliminating unnecessary processes that do not benefit the end customer. Removing waste is essential for process improvement and achieving greater efficiency.
💡 Mapping your value stream is a critical step in creating a Lean management system that promotes speed, quality, and cost-effectiveness. It also supports waste reduction initiatives by making it easier to spot and address inefficiencies.
3. Create Flow
After removing waste, the goal is to create a flow that allows work to move through the production system or service delivery without interruptions.
Creating flow involves:
- Standardizing operations
- Reducing handoffs and queues
- Structuring tasks in a tight sequence
- Creating cross-functional departments to facilitate a smooth flow of work across teams
Flowing smoothly through the system is a sign of an optimized Lean process. The smoother the flow, the faster your organization can respond to customer demand. Training employees in multiple skills is essential for maintaining a smooth workflow and supporting continuous improvement.
📈 The Lean principles provide a clear roadmap for improving workplace efficiency and help improve efficiency across the organization while maintaining high quality standards.
4. Establish a Pull System
The fourth principle is to establish pull inventory systems that respond to actual demand, rather than forecasts. A pull-based system ensures that resources are used only when needed, thereby minimizing the use of raw materials and excess inventory. Pull-based systems are specifically designed to meet the needs of end customers, ensuring that production and inventory processes are aligned with what end customers require.
Key actions:
- Implement Kanban boards or signal systems
- Deliver just the quantities required at the right time
- Connect cross-functional departments to support demand-driven flow
- Ensure requisite materials are available to enable just-in-time delivery
Pull systems limit overproduction and increase responsiveness to market changes. They help limit inventory and align production closely with actual demand.
5. Pursue Perfection
The fifth Lean principle is about striving for excellence through continuous improvement. Organizations are encouraged to continuously evaluate and improve all aspects of their production processes and workflows. Emphasizing ongoing continuous improvements is crucial, as it enables regular refinement of processes, boosts productivity, and helps eliminate non-value-added activities.
To achieve this:
- Encourage team input on inefficiencies
- Use qualitative and quantitative techniques to track progress
- Empower employees through training and leadership support
This principle reinforces the importance of corporate culture in sustaining Lean improvements.
🎓 Learn how to build a culture of continuous learning in our Lean Management course. Includes certification and real-world tools to apply all five Lean principles.
Why the Principles of Lean Matter
The principles of Lean management are more than abstract ideas—they form the operating logic for some of the world’s most efficient and effective organizations, with many of these practices originating from lean manufacturing. The lean philosophy underpins these principles, focusing on eliminating waste, enhancing efficiency, and driving continuous improvement throughout the entire value stream.
By aligning teams around Lean thinking, companies can:
- Reduce lead times and inventory
- Improve product quality and customer service
- Increase employee satisfaction and engagement
- Optimize the supply chain and operations
- Achieve sustainable growth and profitability
- Reduce waste and optimize resources by eliminating non-value-added activities
Whether you’re in manufacturing, services, or digital industries, the five Lean management principles provide a reliable framework for remaining competitive in an ever-changing market.
🧩 Try the GET LEAN Simulation Game to experience Lean principles in action. License includes free Lean training access.
Benefits of Lean Management
Adopting lean management delivers a wide range of benefits that can transform organizations into more efficient and effective enterprises. By applying the five lean principles—defining value, mapping the value stream, creating flow, establishing a pull system, and pursuing perfection—companies can streamline their operations and focus on what truly matters: delivering value to customers.
Implementing lean principles enables organizations to eliminate waste and focus on value-creating activities, resulting in significant cost savings and enhanced resource utilization. As processes become more efficient, teams can deliver products and services faster, with higher quality and fewer errors. This not only boosts customer satisfaction but also enhances the organization’s reputation in the marketplace.
Lean management also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees at all levels to seek out opportunities for optimization and innovation. By regularly mapping the value stream and creating flow, organizations can quickly adapt to changing customer needs and market conditions, ensuring they remain competitive. The pull system further supports this adaptability by aligning production with actual demand, reducing excess inventory and unnecessary work.
Ultimately, the benefits of lean management extend beyond operational efficiency—they create a foundation for sustainable growth, agility, and long-term success.
Applying Lean in Your Organization
Implementing Lean successfully requires more than learning the theory. Lean implementation should focus on waste reduction as a primary objective, driving efficiency and continuous improvement throughout the organization. You must:
- Train employees across all levels
- Support Lean initiatives by training employees to develop multi-skilled, adaptable teams.
- Create systems that support pull-based flow
- Promote accountability through metrics and team collaboration
- Use Lean techniques that align with your industry
🔁 Explore the full learning path with our Continuous Improvement course and Problem Solving course.
Common Challenges in Lean Implementation
While the advantages of lean management are clear, implementing lean principles can present significant challenges, especially in organizations with established routines and mindsets. One of the most common hurdles is resistance to change, as employees may be hesitant to alter familiar processes or adopt new ways of working. Overcoming this resistance requires strong leadership and effective communication about the value and purpose of lean initiatives.
Another challenge lies in shifting the organizational culture to adopt a continuous improvement and customer-centric approach. This often means breaking down silos and encouraging collaboration across departments, as well as empowering employees to identify and eliminate waste within the value stream.
Successful lean implementation also depends on a thorough understanding of the organization’s processes. Teams must be able to accurately map the value stream and utilize both qualitative and quantitative techniques to pinpoint inefficiencies and measure progress. Training and ongoing support are crucial for developing the necessary skills and mindset to foster continuous improvement.
By focusing on the key lean principles and leveraging data-driven decision-making, organizations can navigate these challenges and unlock the full potential of lean management.
Measuring Lean Success
To ensure that lean management efforts are delivering results, it’s essential to establish clear methods for measuring success. Effective measurement allows organizations to track progress, identify areas for further improvement, and make informed decisions based on real data.
Key performance indicators for lean success include lead time, throughput, inventory levels, and defect rates. These metrics provide insight into how efficiently the value stream is operating and where bottlenecks or waste may still exist. Value stream maps are powerful tools for visualizing these metrics and tracking improvements over time.
Beyond operational metrics, organizations should also monitor customer satisfaction, employee engagement, and financial performance to gain a comprehensive view of their lean management system’s impact. Regularly reviewing these indicators supports the principle of continuous improvement, helping teams stay aligned with organizational goals.
Drawing inspiration from the Toyota Production System and the core principles of lean, organizations should foster a culture where data-driven decision-making and ongoing refinement are the norm. By consistently measuring and analyzing performance, companies can pursue perfection and achieve lasting success through lean management.
Final Thoughts: The Enduring Power of Lean Principles
The principles of Lean remain highly relevant for organizations of all sizes. Whether you’re improving a manufacturing process, optimizing software development, or transforming a healthcare system, the five Lean principles offer clarity and structure.
By understanding and applying these Lean management principles, you not only eliminate waste, but you also deliver more value to customers and foster a culture of growth.
🚀 Start mastering the Lean mindset with our certified Lean Management course. Join thousands who’ve built more responsive, cost-effective, and high-performing organizations.
