Principles of Lean Production: Mastering Operational Efficiency in Modern Manufacturing
Introduction: Why Lean Production Principles Still Matter
In a world of digital disruption, globalized markets, and rapidly shifting customer demands, manufacturing companies face relentless pressure to reduce costs, deliver faster, and improve quality. The answer for many is a return to fundamentals—specifically, to lean production principles. Grounded in the practices developed by the Toyota Production System, these principles help companies transform their manufacturing process into a streamlined, value-driven engine.
This article explores how the five lean principles continue to shape manufacturing strategy today. Lean methods are now being applied across industries—including services, healthcare, IT, and the public sector—to address modern challenges and optimize processes. We’ll dive deep into their application, evolution, and results across industries. Whether seeking to reduce waste, maximize efficiency, implement just-in-time systems, or increase customer value, this guide will provide actionable insights grounded in decades of best practices. By leveraging lean principles, organizations can create wealth through improved profitability and operational excellence.
🎓 Want to go beyond theory? Explore our Lean Management Course and start implementing lean strategies with real-world precision.
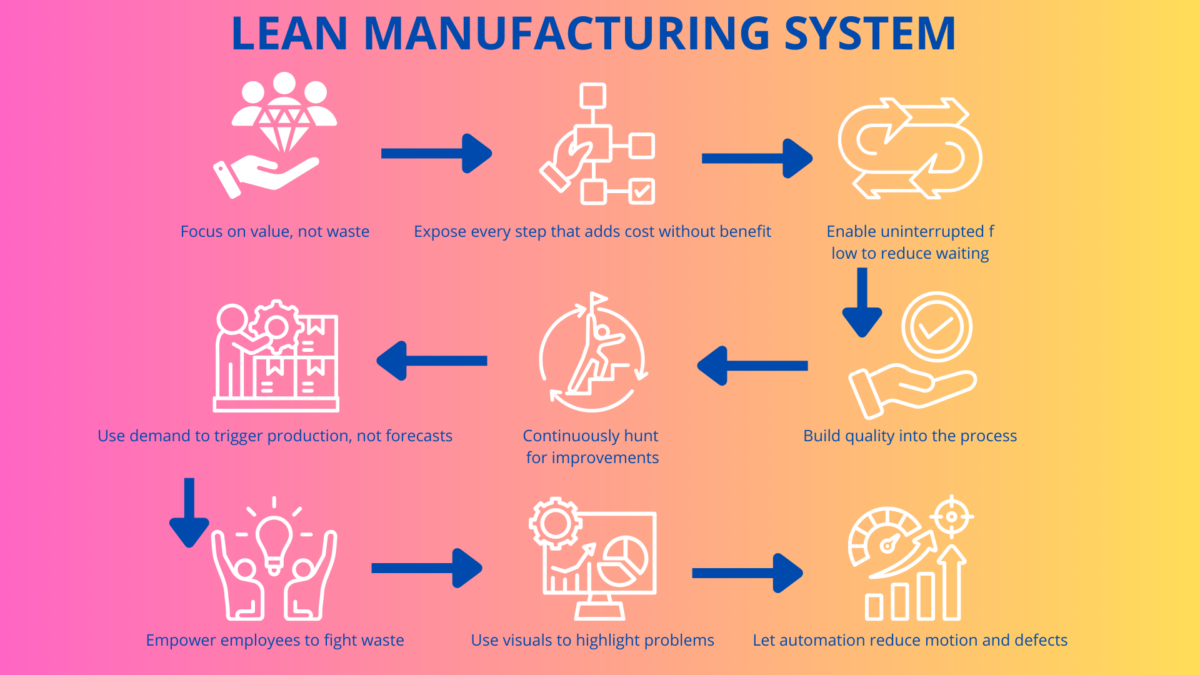
What Are the Principles of Lean Production?
Lean production principles refer to a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating waste (non-value-added activities) through continuous improvement by flowing the product at the pull of the customer. A lean principle is a foundational concept focused on waste reduction and value creation, forming the basis for lean manufacturing methodology. These principles aim to banish waste from production processes to maximize efficiency and value. Lean tools, such as value stream mapping and real-time performance monitoring, are integral to implementing these principles and driving continuous improvement. These principles form the core of lean manufacturing and are used to maximize value while minimizing waste in any production process.
The Five Core Principles
- Define Value – Understand what creates value from the customer’s perspective.
- Map the Value Stream – Identify all steps in the manufacturing process and eliminate those that do not add value.
- Create Flow – Ensure that products move smoothly through production without delays.
- Establish Pull – Produce only in response to customer demand, avoiding excess inventory.
- Seek Perfection – Continuously improve processes to approach ideal performance.
These five principles form the backbone of Lean and align with the methodologies behind the Toyota Production System and modern lean management systems.
Defining Value from the Customer’s Perspective
All lean production principles begin with the question: What is valuable to the customer? This requires understanding the customer’s perspective on a product’s function, quality, price, and delivery. Activities that do not directly support this value are considered waste.
By clearly defining value, organizations can:
- Eliminate unnecessary processes
- Prioritize improvements
- Enhance customer satisfaction
Mapping the Value Stream for Insight and Clarity

A value stream represents every step, both value-adding and non-value-adding, that a product goes through from raw materials to the hands of the customer. Value stream mapping is a core lean manufacturing tool used to visualize and analyze the entire flow, including the whole supply chain from sourcing materials through production to delivery. By mapping the entire supply chain, organizations can identify and eliminate waste at every stage, increasing efficiency. This process also involves a detailed analysis of production processes to optimize workflows further and reduce inefficiencies.
Benefits of Mapping
- Highlights inefficiencies
- Identifies unnecessary movement
- Supports data-driven decisions
🧠 Want to improve your team’s problem-solving capabilities? Our Problem-Solving Course gives you proven tools to tackle root causes with confidence.
Creating Flow in Production Systems
After mapping the value stream, the next challenge is creating flow, ensuring that materials, information, and tasks flow smoothly through the production line. Interruptions or bottlenecks delay production and increase costs.
Lean manufacturing plants are known for achieving high productivity and quality by focusing on waste reduction, continuous improvement, and efficient workflows, often with minimal reliance on advanced plant technology.
Strategies for creating flow include:
- Implementing standard lean production models
- Introducing work cells
- Minimizing batch sizes
- Using just-in-time delivery systems
Lean factories aim for continuous flow that reduces time to market and enhances flexibility.
🔧 Practical tools like 5S are foundational to flow. Check out our 5S Workplace Organization Course for templates and checklists that support lean environments.
Pull Systems and the End of Overproduction
A traditional “push” system is based on forecasts. In contrast, a pull system is produced based on actual customer demand. In Toyota’s approach, production is aligned with actual sales data rather than relying on forecasts, ensuring output matches real market demand. Unlike traditional systems that set fixed production targets, lean manufacturing shifts to a demand-driven model, focusing on continuous improvement and avoiding overproduction. This minimizes excess inventory, reduces space requirements, and enhances flexibility.
Examples include:
- Kanban cards to signal replenishment
- FIFO (First-In, First-Out) lanes
- Demand-driven replenishment models
📦 Interested in applying pull systems? Our Lean Management Course teaches real strategies for implementing them in any production environment.
Seeking Perfection Through Continuous Improvement
The final and most transformative of all lean manufacturing principles is the pursuit of perfection. This requires a commitment to continuous improvement (kaizen), where every employee contributes to identifying problems and improving systems. Continuous improvement is a core aspect of lean, systematically enhancing factory processes, reducing waste, and increasing efficiency.
Organizations that foster a continuous improvement culture benefit from:
- Ongoing productivity gains
- Higher operating performance
- More engaged employees
🔄 Looking to embed this mindset across your team? Our Continuous Improvement Course provides a roadmap for sustainable change.
Lean Management Practices for Sustainable Change
Sustaining improvements in manufacturing requires more than a one-time initiative—it demands a shift in daily management practices rooted in lean principles. Lean management is about embedding continuous improvement into the fabric of your organization, ensuring that every process is regularly evaluated and refined to meet evolving customer demand.
Key lean management practices include:
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Encourage teams to regularly assess and enhance manufacturing processes, driving incremental gains in efficiency and quality.
- Value Stream Mapping: Use this powerful lean manufacturing tool to visualize the entire value stream, pinpointing sources of waste and identifying opportunities to streamline operations.
- Implementing Pull Systems: Align production with customer demand, reduce excess inventory, and ensure resources are used efficiently.
- Creating Smooth Flow: Design manufacturing processes so materials and information move seamlessly from one step to the next, minimizing delays and bottlenecks.
By consistently applying these lean management practices, companies can eliminate waste, improve manufacturing efficiency, and boost customer satisfaction. The result is a culture of sustainable change, where every improvement builds on the last and the entire organization is aligned around delivering value.
Common Challenges in Implementing Lean Production Principles
- Cultural resistance
- Lack of lean leadership
- Misalignment between departments
- Inconsistent metrics
- Some critics argue that lean can negatively impact employee well-being and safety by prioritizing efficiency over human factors.
Overcoming these requires:
- Executive sponsorship
- Cross-functional teams
- Structured coaching
🤝 Want to build effective teams to support lean transformation? Our Teamwork & Leadership Course gives your leaders the skills to drive change collaboratively.
Measuring Success in Lean Production
Progress must be measured using clear, actionable metrics to ensure that lean manufacturing efforts deliver real results. Tracking the right key performance indicators (KPIs) allows organizations to see where lean principles are working and where further improvement is needed.
Common KPIs for lean production include:
- Lead Time: The time it takes for a product to move through the entire value stream, from raw materials to finished goods.
- Inventory Levels: Monitoring inventory helps ensure pull systems and smooth flow, and reduces excess stock and associated costs.
- Defect Rates: Lower defect rates indicate that continuous improvement efforts are enhancing quality across manufacturing processes.
Regular audits and assessments are also vital. These reviews evaluate how well value stream mapping, pull systems, and other lean manufacturing tools are being implemented. Companies can drive continuous improvement by consistently measuring success, ensuring that lean production principles are adopted and sustained for long-term operational excellence.
The Strategic Benefits of Lean Production Principles
Companies that embed lean principles experience measurable benefits:
- Faster manufacturing operations
- Lower costs from reducing waste
- More agile supply chains
- Greater alignment with customer demand
- Enhanced ability to scale efficient processes
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Lean Production
While the benefits of lean production are well-documented, many organizations encounter pitfalls that can undermine their efforts. Avoiding these common mistakes is crucial for achieving the full potential of lean manufacturing.
Key mistakes to watch out for include:
- Failing to Identify Customer Value Accurately: Companies risk investing in unnecessary processes that add no real benefit without clearly understanding what the customer truly values.
- Neglecting the Five Key Principles: Skipping steps or only partially implementing the core principles of lean manufacturing—value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection—can lead to incomplete results.
- Relying on Push Systems: Producing based on forecasts rather than actual customer demand often results in overproduction and excess inventory, counteracting lean goals.
- Overlooking Value Stream Mapping: Without mapping the value stream, it’s challenging to spot sources of waste or areas for improvement, making it harder to implement effective changes.
- Ignoring Lean Management Tools: Failing to leverage lean manufacturing tools and a robust lean management system can stall progress and limit continuous improvement.
By avoiding these pitfalls and focusing on accurately identifying customer value, mapping the value stream, and fully embracing lean principles, organizations can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and achieve higher levels of customer satisfaction. Implementing lean manufacturing tools and fostering a culture of continuous improvement are essential steps on the path to lean production success.
Getting Started with Lean: First Steps
- Educate leadership on the principles of lean
- Begin value stream mapping for one product line
- Launch a pilot pull system with Kanban
- Implement 5S to stabilize work areas
If you’re committed to building a culture of efficiency and sustainable performance, the Lean Management Course is your blueprint. Built on 25 years of practical experience implementing Lean and 5S in some of Europe’s most demanding industries, this course delivers a pragmatic, not theoretical path to lean success. You’ll get fundamental tools, case studies, and lifetime access to proven materials.
🎥 Preview a lesson and discover how Lean can reshape your organization from the ground up.
If you want your team to learn Lean through practice, not just PowerPoint, explore the GET LEAN Simulation Game—an interactive workshop that simulates Lean in action for hands-on engagement and rapid learning.
Your Lean journey starts now. Let’s build a better, faster, smarter operation together.