
The process of lean manufacturing is a structured, systematic approach that helps organizations eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and deliver maximum customer value. As a lean manufacturing methodology, it systematically enhances efficiency and reduces waste across various sectors. Originating from the Toyota Production System (TPS), Lean manufacturing has evolved into a global standard for innovative, efficient, and sustainable production. The origins of lean manufacturing can be traced back to the early 20th century, when scientific management, pioneered by Frederick Winslow Taylor, laid the groundwork for later efficiency and production systems. It’s not just a set of tools—it’s a mindset that transforms the production process across industries. Ultimately, lean manufacturing aims to create wealth by optimizing processes and increasing value.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the whole lean manufacturing process, its principles, techniques, and tools. You’ll learn how to implement Lean manufacturing, understand the role of the value stream, and see how companies achieve continuous improvement by applying the lean production system.
What Is Lean Manufacturing?
Lean manufacturing is a production system and management methodology focused on eliminating all forms of waste (muda) while maximizing value for the customer. It aims to reduce production costs, optimize the manufacturing process, and respond quickly to customer demand. Lean manufacturing principles are the core guidelines that drive this approach, focusing on reducing waste, enhancing efficiency, and promoting continuous improvement.
The term Lean manufacturing refers to a philosophy that promotes efficiency by focusing on only what adds value from the customer’s perspective. It encourages just-in-time manufacturing, streamlined processes, and continuous process improvement. Lean methods are the practical tools and techniques used to implement lean manufacturing in various industries.
🎓 Want to implement Lean in your organization? Enroll in our certified Lean Management course—learn at your own pace and gain practical tools based on real-world projects.
Lean manufacturing plants worldwide have adopted these principles to achieve higher productivity and quality.
The Five Key Principles of Lean Manufacturing
The five key principles form the foundation of the standard Lean production model, as defined by the Lean Enterprise Institute and widely used in manufacturing facilities and service sectors alike. A lean principle is a core value or guideline that drives waste reduction and continuous improvement within production processes.
1. Identify Value
From the customer’s perspective, value is what they are willing to pay for. Everything else is waste.
2. Map the Value Stream
Use value stream mapping to identify every step in your production line—mapping value streams is a fundamental step in lean manufacturing. A value stream map is a visual tool used to identify inefficiencies and improve operational flow. Mapping should start from raw materials and follow the process through to final delivery. Eliminate non-value-adding steps.
3. Create Flow
Ensure that the value stream moves smoothly without delays, interruptions, or bottlenecks. Creating flow means removing functional barriers within manufacturing to ensure that processes operate smoothly and maintain a consistent, uninterrupted stream of work or materials throughout the production cycle. Value flow refers to the seamless movement of value through the production process, eliminating any obstacles that could disrupt efficiency. Lean processes are designed to support continuous, uninterrupted flow and minimize waste, aligning with lean manufacturing principles for higher productivity and quality.
4. Establish a Pull System
Only produce what is needed, when it is needed. Establish a pull system based on real customer demand. This approach replaces traditional production targets with schedules that respond directly to actual customer orders.
5. Pursue Perfection
Engage in continuous improvement, seeking incremental improvements every day.
These principles of Lean manufacturing are not a one-time fix—they are a continuous flow of improvement activities.
The Lean Manufacturing Process Step by Step
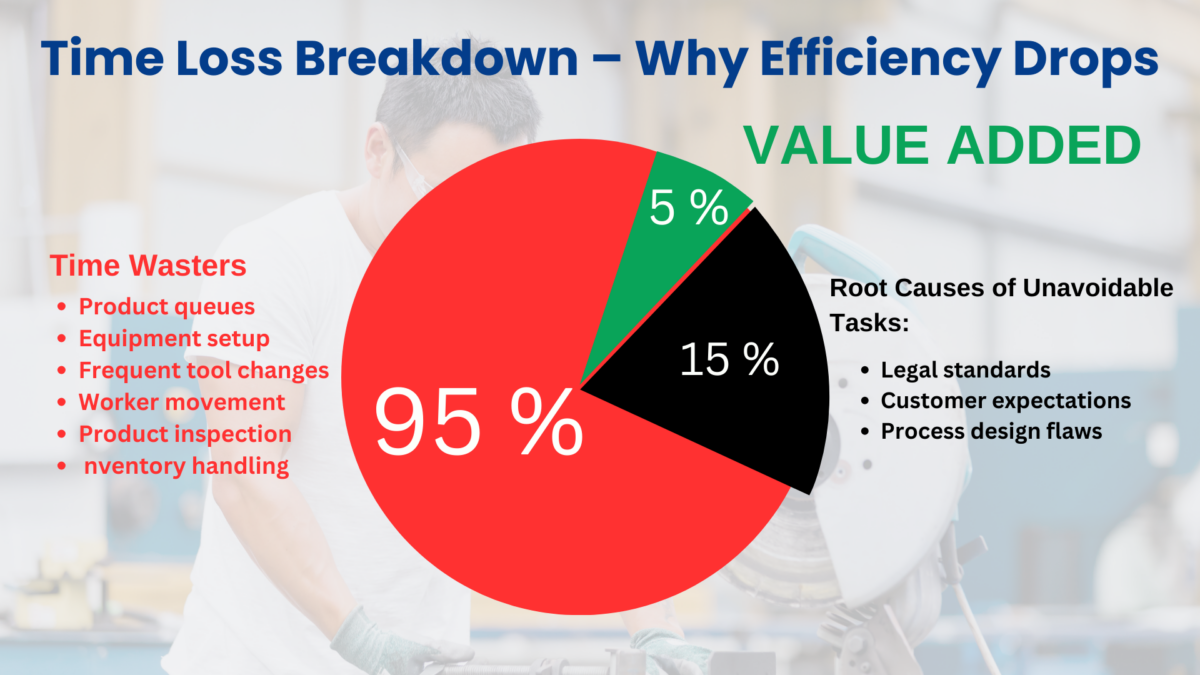
The process of Lean manufacturing is implemented in several stages:
Step 1: Analyze the Current State
- Conduct a Lean assessment, evaluating current productive processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Use value stream mapping to analyze how materials and information flow.
Step 2: Identify Wastes
- Use the eight wastes framework: overproduction, waiting, transport, over-processing, excess inventory, motion (unnecessary movement is a key example of motion waste), defects, and unused talent.
- Involve shop floor workers to locate wasted resources.
Step 3: Redesign Processes
- Apply lean manufacturing techniques to streamline workflows, implementing process improvements to eliminate waste and enhance efficiency.
- Introduce Lean manufacturing tools, including 5S, SMED, Kanban, and TPM.
Step 4: Implement Pull Systems
- Shift from push-based scheduling to demand-driven production.
- Adopt just-in-time delivery strategies.
Step 5: Standardize and Sustain
- Create standard operating procedures.
- Utilize Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) to maintain equipment efficiency.
Step 6: Monitor and Improve
- Use KPIs like cycle time, throughput, and customer satisfaction.
- Reinforce continuous improvement through employee engagement.
📦 Want to see this in action? The GET LEAN Simulation Game offers hands-on practice in Lean principles. Includes free course access with every license.
Core Tools and Techniques in Lean Manufacturing
Value Stream Mapping
This technique helps identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and opportunities for reducing waste, enabling organizations to minimize waste throughout their production processes.
Kanban Systems
A visual pull system that signals when new materials or tasks are needed.
5S Methodology
Focuses on workplace organization: Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain.
Standard Work
Ensures consistency across shifts and teams.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
A proactive approach to maintaining equipment reliability.
These Lean manufacturing tools are essential for building resilient production systems.
💡 Learn how to use these tools with expert guidance in our Lean Management course.
How to Implement Lean Manufacturing in Your Company
To implement Lean manufacturing effectively and apply lean principles throughout the organization:
- Secure leadership support
- Train cross-functional teams
- Start with a pilot area
- Use real data to make decisions
- Promote a culture of problem-solving
- Celebrate small wins and learn from failures
📘 Our Problem Solving course teaches structured methods for tackling root causes and preventing recurrence.
Applying Lean Principles to the Supply Chain
Applying lean principles to the supply chain is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their entire manufacturing process and deliver enhanced customer satisfaction. By implementing lean manufacturing techniques throughout the supply chain, companies can systematically reduce waste, streamline operations, and ensure that every step adds value from the customer’s perspective.
A key strategy is to map the value stream across the supply chain, identifying non-value-added activities and opportunities to reduce waste. This enables businesses to focus on only what is necessary, minimizing excess inventory and unnecessary movements. Implementing pull systems ensures that materials and products are produced and delivered just in time, based on actual customer demand, rather than forecasts. This approach not only reduces production costs but also improves responsiveness to market changes.
Total productive maintenance plays a vital role in supporting lean supply chain operations by maximizing equipment reliability and minimizing downtime, thereby maintaining a smooth flow of materials. Just-in-time delivery further enhances efficiency by reducing inventory holding costs and ensuring that resources are available exactly when needed.
By applying lean principles to the supply chain, organizations can create a more agile, cost-effective, and customer-focused manufacturing process. The result is a supply chain that supports continuous improvement, reduces waste, and consistently delivers value to the customer.
Real-World Lean Manufacturing Examples
Many industries have benefited from Lean manufacturing examples by adopting various lean methods to achieve results:
- Automotive industry: Toyota, Ford, and Honda
- Electronics: Intel and Sony
- Healthcare: Reducing patient wait times and errors
- Logistics: Streamlining packaging and shipping
These cases prove that Lean is not just a theory—it’s a proven system that adapts to various sectors.
Benefits of the Lean Manufacturing System
Implementing the Lean manufacturing system helps organizations:
- Improve inventory management
- Lower production cycle times
- Align processes with customer demand
- Reduce excess inventory
- Improve safety and employee morale
- Enhance the work environment through better organization and streamlined workflows
- Respond flexibly to changes in the supply chain
🧩 Ready to transform your production? Enroll in our Lean Management course and master the tools used by world-class organizations.
Challenges of Lean Manufacturing
While the benefits of lean manufacturing are significant, implementing lean principles presents its challenges. One of the most common obstacles is transforming the organizational culture to embrace continuous improvement and empower employees at all levels. This cultural shift requires strong leadership and a commitment to lean thinking, which can be challenging to achieve, especially in companies with deeply rooted traditional practices.
Identifying and eliminating waste across complex manufacturing processes can also be a daunting task. It often involves detailed analysis and collaboration across departments, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. In large-scale production environments, maintaining the flexibility and adaptability required by lean manufacturing can be particularly challenging.
Another potential pitfall is the risk of prioritizing efficiency and cost reduction over quality or customer satisfaction. Lean manufacturing aims to reduce waste, but not at the cost of delivering value to the customer. Striking the right balance is essential for long-term success.
To overcome these challenges, organizations must invest in ongoing training and education, foster a culture of open communication, and encourage problem-solving at every level. By staying committed to continuous improvement and effectively implementing lean principles, companies can navigate these obstacles, improve their manufacturing processes, and achieve higher levels of customer satisfaction.
The Role of Lean Thinking in Long-Term Success
Lean thinking emphasizes that improvement is an ongoing process, never truly finished. Companies must:
- Continuously improve manufacturing processes
- Focus on adding value, not just cutting costs
- Train lean employees to think proactively
- Build a high-performance supplier network
- Use metrics to measure progress
While cutting waste is essential in lean manufacturing, it should be balanced with maintaining long-term growth and fostering innovation to avoid jeopardizing future development.
👥 Want to improve how your teams work together? Our Teamwork and Leadership course enhances collaboration in Lean environments.
Final Thoughts
The process of Lean manufacturing is about more than tools or techniques—it’s a way of thinking and operating. It integrates Lean principles, customer value, and continuous improvement, highlighting the importance of lean processes in achieving operational excellence by minimizing waste and streamlining production.
By applying the principles of Lean, using proven tools like value stream mapping, and following the Toyota Production System TPS, companies can eliminate waste, reduce costs, and increase satisfaction for customers and employees alike.
🚀 Get started today with the Lean Management course, and boost your team’s ability to apply Lean across all aspects of production. Includes lifetime access, certification, and real-world examples.
