Training on Lean Manufacturing: The Key to Sustainable Excellence

In today’s hyper-competitive market, companies can no longer afford inefficiencies, delays, or quality issues. Customers demand more value, faster delivery, and greater flexibility, leaving organizations under pressure to do more with less. This is where training on lean manufacturing proves its worth, equipping professionals with the skills, knowledge, and mindset to transform operations from the inside out.
Implementing Lean Six Sigma within a company can significantly enhance company culture, boost operational efficiency, and improve overall performance by streamlining processes and reducing waste.
Lean manufacturing is not just about cutting costs—it’s about creating more value with fewer resources. However, successful implementation requires more than enthusiasm; it demands structured education, team alignment, and practical application.
This article explores why lean training is vital, what it includes, who should take it, and how it impacts everything from the manufacturing process to customer satisfaction.
What Is Training on Lean Manufacturing?
Training on lean manufacturing refers to structured learning programs that teach the fundamentals and practical applications of Lean principles in a production or operational environment. These training initiatives help employees:
- Understand and identify waste (muda)
- Streamline production processes
- Enhance collaboration across teams
- Deliver greater value to customers
- Sustain long-term improvements through standardization
Lean training may include workshops, online courses, on-site coaching, or certification programs. Many modern organizations also combine Lean with Six Sigma tools for data-driven process optimization, leveraging the Six Sigma methodology as a structured approach to process improvement, defect reduction, and operational excellence. The sigma methodology emphasizes systematic waste elimination and quality management for continuous improvement and cost reduction.
Why Is Lean Training Important?
No matter how advanced your machinery or software is, operational excellence begins with people. Lean training empowers your workforce to:
- Improve productivity through more brilliant work design
- Reduce lead times and rework
- Create flow and eliminate bottlenecks
- Build stronger connections between departments and suppliers
- Improve service levels and customer outcomes
🎓 Looking for a structured way to train your team in Lean principles? Discover our Lean Management – Practical Course that turns concepts into action.
Core Elements of a Lean Manufacturing Training Program
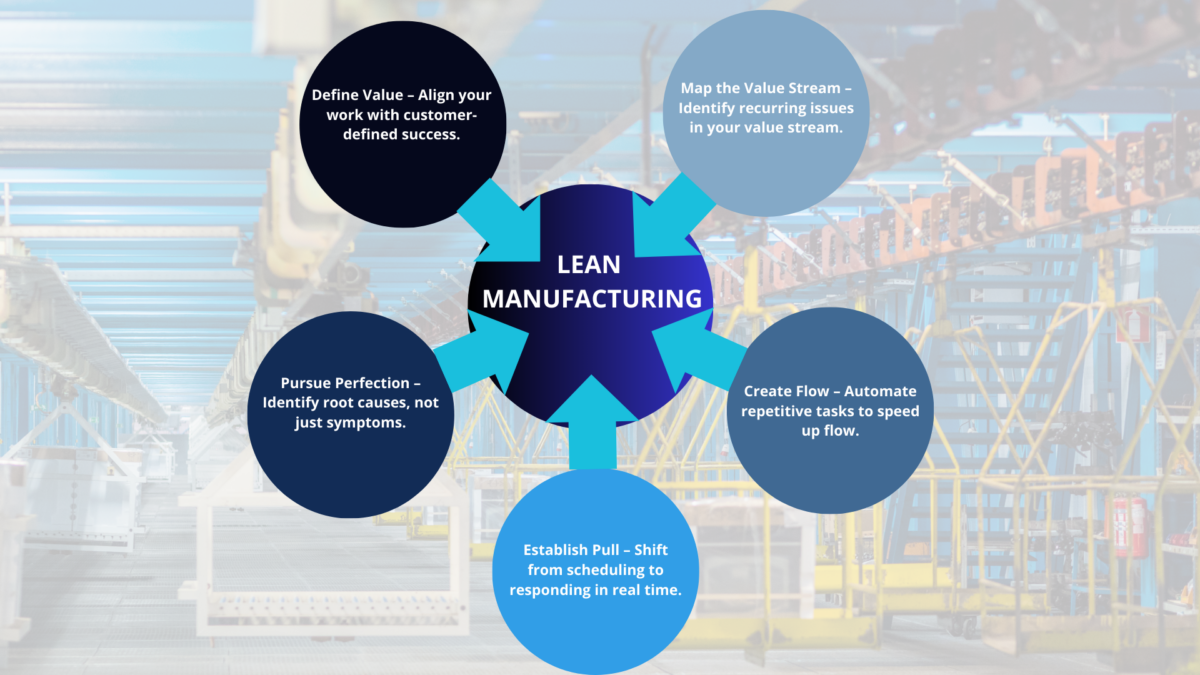
A practical Lean training course typically includes the following components:
1. Lean Principles and the Toyota Production System
Participants learn the five core Lean principles: defining value, mapping the value stream, creating flow, establishing pull, and pursuing perfection. These form the foundation of implementing lean principles across any process.
2. Identifying the 8 Wastes
Understanding and removing waste is central to Lean. Training teaches how to spot the eight types of muda—overproduction, waiting, transport, overprocessing, inventory, motion, defects, and unused talent—and how to eliminate them.
Lean and Six Sigma methodologies are designed to minimize and reduce manufacturing process defects, improving efficiency and product quality.
3. Standard Work and Visual Management
Standardized processes reduce variability and enable consistent performance. Learners explore how visual controls support efficiency and ownership.
4. Problem Solving and Root Cause Analysis
Participants develop critical thinking skills using Lean tools like A3 Thinking, fishbone diagrams, and the 5 Whys—building capability to fix the root cause rather than symptoms.
🔍 Ready to go deeper into structured root cause analysis? Take a look at our Problem Solving course.
5. Flow and Pull Systems
Training emphasizes the importance of smooth process flow and producing based on demand (not forecasts), which improves agility and reduces inventory holding costs.
6. Kaizen and Continuous Improvement
Teams are encouraged to constantly challenge the status quo, using small, incremental changes to make significant performance gains over time.
🔁 Want to embed CI into your daily work routines? Our Continuous Improvement course shows how to make it part of your team culture.
The Role of Lean Training in the Manufacturing Process
Lean training doesn’t happen in a vacuum. It directly impacts the production of products and services and team collaboration.
Through hands-on application and real-world examples, trainees learn to:
- Redesign process flows
- Set up cells and U-shaped lines
- Reduce setup times (SMED)
- Improve throughput and first-pass yield
- Integrate quality into each step of the manufacturing process
Lean-trained professionals don’t just understand the “how” of manufacturing—they know the “why” behind every process step.
Lean Six Sigma certification programs are designed to enhance an organization’s processes by providing customized training at various levels and fostering teamwork.
Quality Control in Lean Manufacturing
Quality control is a cornerstone of lean manufacturing, ensuring that every product meets customer requirements and is defect-free. Organizations can systematically minimize errors and eliminate waste throughout their manufacturing processes by implementing lean principles and leveraging tools such as statistical process control and total productive maintenance.
Lean manufacturing training strongly emphasizes continuous improvement and encourages employee involvement in quality control activities. This collaborative approach helps identify and resolve quality issues at their source and fosters a culture of accountability and pride in workmanship.
Effective quality control in lean manufacturing extends beyond the factory floor. It requires robust supply chain management to guarantee that all raw materials and components meet stringent quality standards before entering production. Organizations can significantly reduce rework, scrap, and warranty claims costs by focusing on quality at every stage, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Integrating quality control into lean processes ultimately empowers organizations to deliver superior products, reduce waste, and achieve sustainable operational excellence.
Lean Six Sigma Certification: A Logical Next Step
While Lean focuses on flow and waste, Six Sigma emphasizes variation and data-driven decisions. Many organizations choose to combine both through Lean Six Sigma certification programs.
These certification tracks include:
- Yellow Belt – Introductory level for team members
- Green Belt – For those leading smaller improvement projects
- Black Belt – Advanced level for CI professionals and managers
- Master Black Belt – Strategic leaders and trainers
Sigma training covers these different certification levels and is often tailored to meet the needs of manufacturing organizations, focusing on customized learning and process improvement.
A Lean Six Sigma certification demonstrates deep knowledge in problem-solving and process control, making it ideal for leaders of high-stakes projects. Completing the required projects and coursework is necessary to achieve advanced certification at the Black Belt level.
📌 Looking to certify your staff? Many lean training courses now offer bundled certification programs to validate learning and recognize achievement.
Lean Six Sigma certification is a valuable professional asset, enhancing one’s career prospects and reputation within organizations.
How Lean Training Builds Supply Chain Resilience
Lean isn’t confined to your factory floor—it stretches across your entire value chain. Training in Lean also equips participants to optimize supply chain management by:
- Creating more substantial alignment with suppliers
- Applying Lean inventory practices (Kanban, JIT)
- Streamlining logistics and transportation
- Reducing variability and delays
- Responding faster to changes in customer demand
By improving internal processes and external collaboration, Lean supports a faster, more flexible, and more reliable supply chain.
Who Should Attend Lean Manufacturing Training?
Lean training is valuable for anyone involved in operational work or process improvement. This includes:
| Role | How They Benefit |
|---|---|
| Line Operators | Learn to identify and eliminate waste in real-time |
| Supervisors | Lead teams through standardization and improvement |
| Engineers | Apply Lean in design, layout, and quality systems |
| Managers | Align Lean efforts with strategic goals |
| Supply Chain Staff | Build flow and responsiveness |
| Trainers and HR | Support lean onboarding and culture building |
Some organizations train entire departments, while others integrate Lean learning into leadership development or technical upskilling programs.
Course Delivery Formats
Lean training is now more accessible than ever, with delivery options such as:
- Online video courses (VoD)
- Virtual instructor-led workshops
- In-person factory floor coaching
- Hybrid learning with tools and simulations
Many online Lean Six Sigma courses also include discussion forums to foster interactive engagement and peer learning.
💡 Want flexible learning that scales with your team? The Lean Management – Practical Course includes lifetime access and real templates, perfect for onboarding and ongoing development.
Practical Outcomes of Lean Training
After completing Lean training, participants typically report:
- Better ability to diagnose process issues
- Confidence in leading improvement initiatives
- Improved collaboration across departments
- Lower error rates and rework
- Clearer standards and role expectations
- Enhanced customer satisfaction through better service and product quality
Achieving a Six Sigma level of quality increases customer satisfaction by reducing defects and improving product quality.
Most importantly, trainees become agents of change, able to contribute to the organization’s Lean journey long after the training ends.
Job Opportunities with Lean Manufacturing
Adopting lean manufacturing has created many job opportunities for individuals skilled in lean principles and process improvement across the manufacturing industry. From production line workers to management roles, professionals who understand how to lead lean transformation and drive process optimization are in high demand.
Earning a Lean Six Sigma certification or similar credentials can open doors to specialized positions such as lean coordinator, quality engineer, or supply chain manager. These roles require expertise in problem solving, process improvement, and practical communication skills, which are highly valued in organizations committed to continuous improvement and operational excellence.
As organizations increasingly seek to implement lean methodologies, there is also significant potential for career advancement. Individuals who gain knowledge and hands-on experience in lean manufacturing can move into leadership positions, guiding teams through successful lean transformations and contributing to their organizations’ overall success.
By investing in lean training and certification, professionals increase their earning potential and job satisfaction and become valuable assets capable of driving meaningful change and delivering lasting results.
From Theory to Practice: Learning Through Simulation
Simulation games are one of the most effective methods for teaching Lean, particularly for teams unfamiliar with Lean concepts.
🎮 Try the GET LEAN Simulation Game to practice process redesign, takt time analysis, and teamwork in a competitive and interactive format—ideal for team-building or kaizen workshops.
Best Practices for Lean Manufacturing
Achieving success with lean manufacturing requires more than understanding the theory—it demands a commitment to best practices that drive real results. At the heart of these practices is implementing lean principles, such as eliminating waste and optimizing operations, to boost efficiency and reduce costs.
Continuous improvement is essential, with organizations regularly conducting kaizen events and root cause analysis to identify and solve problems at their source. Encouraging open communication and involving employees at all levels ensures that valuable knowledge and innovative ideas are harnessed to improve processes and quality.
Investing in employee training and development is another critical best practice. By equipping teams with the skills and knowledge needed to apply lean tools and methods, organizations empower their workforce to sustain improvements and adapt to changing demands.
By following these best practices, companies can achieve significant gains in productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction, ensuring they remain competitive in the ever-evolving manufacturing industry.
Choosing the Right Lean Certification Program
When selecting a training provider or certification program, consider:
| Criteria | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Instructor Experience | Real-world background in Lean implementation |
| Tools Provided | Templates, checklists, audit forms, SOPs |
| Case Studies | Examples from your industry or operations type |
| Access | Lifetime login, downloadable materials |
| Format | VoD, live coaching, hybrid |
Lean training should be practical, relevant, and results-oriented—not just theory or jargon.
Common Challenges in Lean Manufacturing
While the benefits of lean manufacturing are substantial, organizations often encounter several challenges on their lean journey. Resistance to change, lack of employee engagement, and insufficient training can hinder the implementation of lean principles and tools successfully.
Navigating the complexities of supply chain management and applying advanced methodologies like Six Sigma can also present obstacles, especially for organizations new to process improvement. Maintaining momentum for continuous improvement and minimizing waste and variability requires ongoing commitment and expertise.
Organizations should build a strong lean culture to overcome these challenges, invest in comprehensive training, and provide continuous support and guidance. Engaging external experts or consultants can also help bridge knowledge gaps and accelerate lean transformation.
By proactively addressing these common hurdles, organizations can unlock the full potential of lean manufacturing and drive sustained performance, quality, and competitiveness improvements.
Future of Lean Manufacturing
Rapid technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability are shaping the future of lean manufacturing. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and advanced data analytics enable organizations to optimize operations, make informed decisions, and drive continuous improvement across their manufacturing processes.
As environmental responsibility becomes increasingly essential, lean manufacturing will focus on reducing waste, minimizing environmental impact, and promoting sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. Collaboration and partnership between organizations will also enhance supply chain management and reduce costs.
By embracing these trends and integrating new technologies, organizations can achieve manufacturing excellence—delivering higher-quality products, reducing costs, and increasing customer satisfaction. Staying ahead of the curve in lean manufacturing means continuously evolving, optimizing processes, and fostering a culture of innovation and improvement.
Final Thoughts: Invest in Capability That Lasts
Training in lean manufacturing is not just about learning a set of tools—it’s about changing how people think, work, and collaborate. By investing in Lean education, organizations build internal capacity to solve problems, improve processes, and deliver consistent customer value.
Lean is a journey, and it starts with learning.
🎓 Take the First Step: Practical Lean Training That Delivers Results
Enroll in our Lean Management- Practical Course if you’re ready to move from scattered improvements to systematic excellence.
🎥 Watch when it suits you – anytime, anywhere
♾️ Full access for life – perfect for ongoing team learning
🧰 Lean tools included – from audits to visual management
🏭 Developed by experts with decades of experience
👉 Sample a free video lesson before signing up
