What Are Business Improvement Techniques? A Comprehensive Guide
Organizations must continually evolve to remain competitive in today’s dynamic business environment. Business process improvement methodologies and business process improvement techniques are structured approaches organizations use to enhance performance, increase efficiency, and optimize workflows. Business improvement techniques are structured methodologies to strengthen various aspects of a business, from operational efficiency to customer satisfaction. These techniques focus on optimizing business processes, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, and driving sustainable growth. Business leaders are crucial in driving these initiatives, ensuring process improvements align with organizational strategy. By implementing these techniques, organizations can achieve their business goals, such as improved efficiency, employee satisfaction, and overall success.
Understanding Business Improvement Techniques
At their core, business improvement techniques involve a systematic approach to improving business processes, identifying, analyzing, and executing strategies that enhance multiple business dimensions. This includes refining processes, identifying areas for improvement, and optimizing processes by analyzing the current process, refining existing processes, eliminating inefficiencies, and aligning operations with organizational goals. By implementing these techniques, businesses can achieve operational excellence and deliver greater customer value.
Business Process Management
Business Process Management (BPM) is a comprehensive approach to overseeing and enhancing an organization’s business processes. BPM enables organizations to achieve greater operational efficiency and customer satisfaction by systematically analyzing, designing, implementing, and monitoring business processes. Companies can streamline workflows, eliminate unnecessary steps, and improve department productivity through BPM. Standardizing business processes with BPM reduces errors and increases transparency, making tracking performance and ensuring consistency easier. Additionally, BPM empowers organizations to quickly adapt their business processes in response to evolving market demands and customer expectations, supporting agility and long-term success.
Key Methodologies in Business Improvement
Business process improvement methodologies and techniques form the foundation of effective business improvement strategies. These structured approaches and specific methods help organizations evaluate, enhance, and optimize their workflows to increase efficiency and performance.
Several methodologies underpin effective business improvement strategies:
Project management is another essential methodology that supports business improvement by helping organizations plan, execute, and monitor projects to achieve their goals efficiently.
2.1 Lean Manufacturing
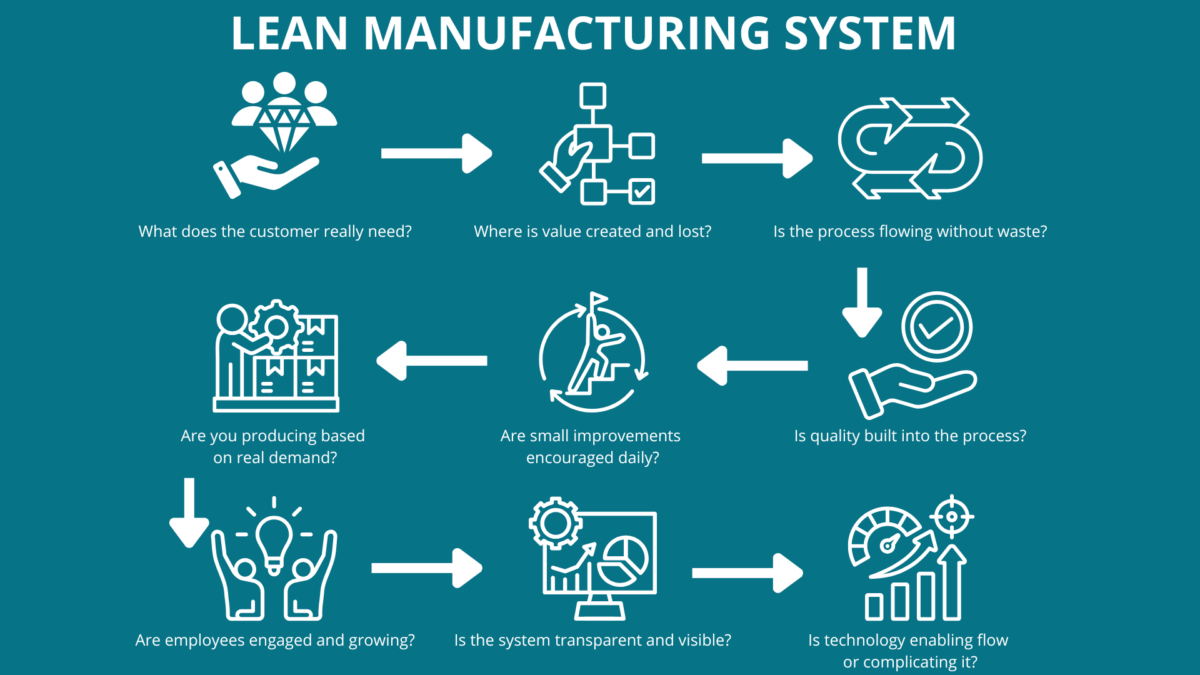
Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing value in production processes. Standardizing processes and streamlining workflows are key goals of Lean Manufacturing, helping organizations reduce inefficiencies and improve productivity.
2.2 Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that uses statistical analysis to reduce defects and improve quality. It provides a structured, data-driven approach to process improvement, focusing on defect reduction and operational excellence.
1. Lean Manufacturing
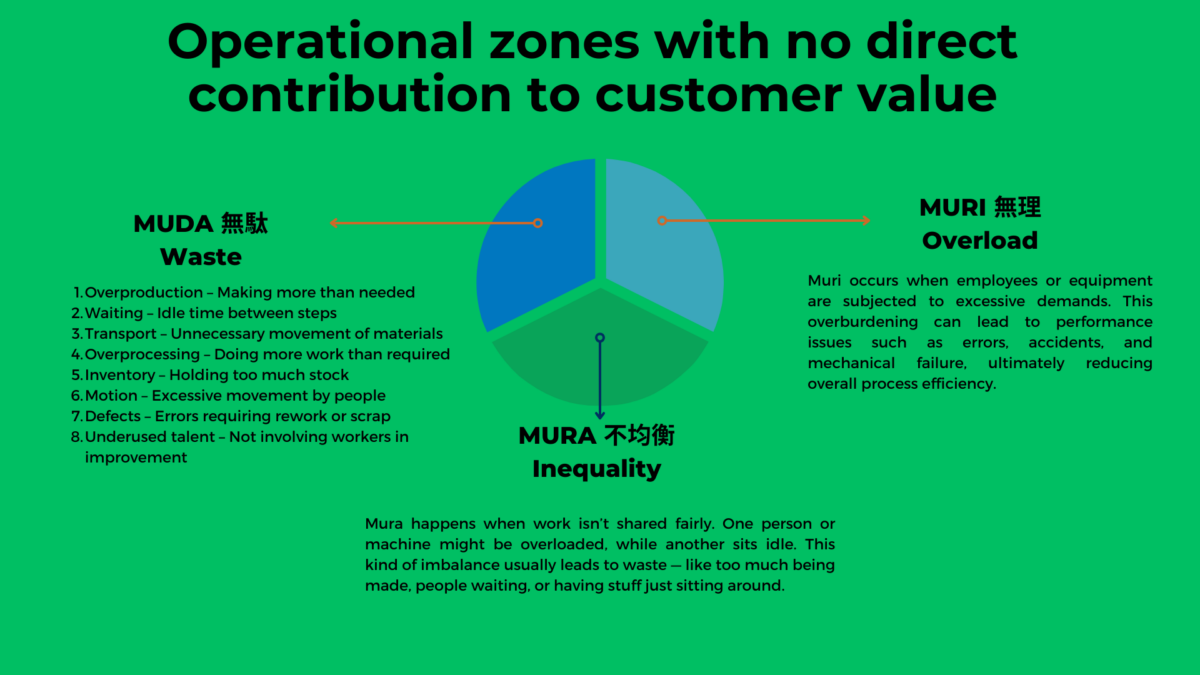
Originating from the Toyota Production System, lean manufacturing is built around eliminating waste and optimizing workflows. Lean aims to eliminate waste and focus on minimizing waste in manufacturing processes by identifying and removing non-value-added activities.
Organizations can streamline production processes and enhance efficiency by focusing on value-added activities and minimizing non-essential tasks.
2. Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a sigma methodology that aims to reduce process defects and variability through a structured, data-driven approach. Utilizing the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework, Six Sigma helps organizations improve quality and achieve process improvement. Statistical analysis is a critical component within Six Sigma, especially in the Measure and Analyze phases, to identify process variations and root causes. Six Sigma supports data-driven decision-making by leveraging performance metrics and thorough data analysis to guide improvements. The DMAIC and DMADV frameworks within Six Sigma are also used to develop new processes that enhance quality and efficiency.
3. Total Quality Management (TQM)
TQM is a holistic approach that integrates quality principles and quality control into every aspect of an organization. Continuous process improvement and improving quality are central goals of TQM, aiming to enhance customer satisfaction and reduce errors through ongoing, data-driven efforts. Employee performance also plays a critical role in TQM, as engaging and evaluating team members supports achieving quality objectives. TQM enhances customer satisfaction and operational performance by fostering a culture of continuous improvement and involving all employees in quality initiatives. Success metrics are used to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of TQM initiatives, ensuring that desired outcomes are achieved.
4. Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
BPR involves radically redesigning core business processes to improve performance and achieve significant improvements in productivity and efficiency. By rethinking existing workflows, organizations can eliminate redundancies, optimize resource utilization, and enhance resource allocation to minimize waste and maximize value. Ultimately, BPR can substantially reduce costs by streamlining operations and eliminating inefficiencies.
Tools and Techniques for Business Improvement
Implementing business improvement strategies often involves various business process improvement techniques and tools:
- Process Mapping: Creating process maps and a process map as visual tools to represent workflows, identify bottlenecks, and highlight areas for enhancement.
- Root Cause Analysis: Identifying the underlying causes of problems to implement practical solutions.
- Value Stream Mapping: Analyzing the flow of materials and information to optimize the value stream.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Metrics used to measure the effectiveness of improvement initiatives.
- Continuous Improvement Cycles: Frameworks like PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) to facilitate ongoing enhancements.
- Automate Manual Work: Using technology to automate manual work, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
- Streamline Workflows: Applying these techniques to streamline workflows, improve efficiency, and enhance organizational performance.
Current State Assessment
A thorough current state assessment is a foundational step in any business process improvement initiative. This assessment involves a detailed analysis of current processes to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for process improvement. By leveraging process mapping, organizations can visually represent their business process, making pinpointing areas that require attention easier. Collecting relevant data and engaging key stakeholders through interviews or workshops ensures a comprehensive understanding of current processes. The outcome is a clear baseline that highlights strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, providing the necessary insights to guide future business process improvement efforts.
Gap Analysis
Gap analysis is a strategic technique used to compare the current state of a business process with its desired future state. By examining current processes and identifying the gaps between where the organization is now and where it wants to be, gap analysis uncovers specific areas that need improvement. This process highlights the magnitude of these gaps and helps prioritize which issues to address first based on their impact and feasibility. Developing potential solutions to bridge these gaps is a key outcome of gap analysis, resulting in a targeted roadmap for business process enhancements that align with organizational goals.
Implementing Business Improvement Techniques
Effective implementation of business improvement techniques requires a structured approach:
- Assessment: Evaluate current business processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Planning: Develop a comprehensive plan outlining objectives, methodologies, and resources, focusing on optimizing resources for maximum efficiency.
- Execution: Implement the chosen improvement strategies, including introducing a new process where necessary, ensuring stakeholder engagement, and actively implementing improvements to address identified gaps.
- Monitoring: Track progress using performance metrics and adjust strategies as needed.
- Sustainability: Foster a culture of continuous improvement to maintain and build upon gains, ensuring the process evolves to adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
Building a Culture of Improvement
Creating a strong culture of improvement is essential for sustaining successful business process improvements over time. This involves empowering employees at all levels to identify areas for improvement, propose solutions, and actively participate in improvement initiatives. Encouraging continuous improvement helps foster a mindset where process improvements are part of everyday work, not just one-time projects. Organizations can support this culture by providing training, resources, and incentives that motivate the team to engage in improvement efforts. Establishing transparent governance and support structures ensures that improvement initiatives align with business objectives and that employees feel supported in improving processes and driving innovation.
Benefits of Business Improvement Techniques
Adopting business improvement techniques offers numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined processes lead to faster turnaround times and reduced costs.
- Improved Quality: Focus on quality management, which results in superior products and services.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Meeting and exceeding customer expectations fosters loyalty.
- Cost Savings: Eliminating inefficiencies and optimizing processes results in significant cost savings for the organization.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Process improvements directly improve customer experience by streamlining interactions and boosting satisfaction.
- Business Improvements: These techniques drive continuous business improvements across all areas of the organization.
- Minimizing Waste: Applying lean management principles helps reduce waste, improve efficiency, and increase customer value.
- Employee Engagement: Involving employees in improvement initiatives boosts morale and productivity.
- Competitive Advantage: Continuous innovation positions organizations ahead of competitors.
Real-World Applications
Businesses across various industries have successfully implemented improvement techniques that benefit not only internal teams but also external stakeholders such as customers and investors:
- Manufacturing: Companies have utilized lean manufacturing to reduce waste and enhance production efficiency.
- Healthcare: Hospitals have adopted Six Sigma to minimize errors, address customer complaints, and reduce human error, improving patient care.
- Finance: Banks have implemented process improvement strategies to streamline operations and enhance customer service.
Sustaining Improvement
Sustaining improvement is crucial to ensuring that the benefits of business process improvements are maintained and built upon over time. This requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation of improved processes to ensure they continue to deliver value and align with organizational goals. Organizations can quickly identify areas for further improvement and address any emerging challenges by tracking key performance indicators and regularly reviewing process performance. Providing continuous training and recognizing employee contributions to improvement efforts helps maintain momentum and encourages a culture of ongoing process improvements. Through sustained focus and adaptation, organizations can ensure that their business processes remain efficient, effective, and responsive to changing needs.
Conclusion
Understanding and applying business improvement techniques is crucial for organizations aiming to thrive in today’s competitive landscape. By embracing lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, and TQM, businesses can optimize operations, deliver superior value, and achieve sustainable growth.
For those interested in deepening their understanding and application of these techniques, consider exploring the following courses:
- Lean Management: Gain insights into implementing lean principles to enhance efficiency.
- Effective Problem-Solving Process: Learn methodologies for identifying and addressing root causes of issues.
- The Fundamentals of 5S: Understand the 5S methodology to organize and maintain a productive workspace.
- Continuous Improvement: Explore strategies for fostering a culture of ongoing enhancement.
- Effective Teamwork and Leadership: Develop skills to guide teams through improvement initiatives.
By investing in these educational resources, organizations can equip their teams with the knowledge and skills to drive meaningful, lasting improvements.
