Spis treści
Lean MFG: Streamlining Manufacturing Processes for Operational Excellence
In today’s competitive industrial landscape, Lean Manufacturing (Lean MFG) has emerged as a pivotal methodology for organizations aiming to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and deliver superior customer value. Lean manufacturing originated from the lean production system developed by Toyota Motor Corporation in the automotive industry, revolutionizing manufacturing practices worldwide.
Rooted in the Toyota Production System (TPS), Lean MFG emphasizes eliminating non-value-adding activities, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, and optimizing the entire production process. The lean production system evolved from earlier concepts such as scientific management, pioneered by Frederick Winslow Taylor, and was further developed by Japanese innovators like Taiichi Ohno and Shigeo Shingo. Over time, the lean philosophy has expanded beyond the automotive industry, influencing modern manufacturing and management approaches across various sectors.
Understanding Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing is a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating waste within manufacturing systems. Lean manufacturing methodology is built on underlying and core principles guiding process improvement. The goal is to achieve efficient processes that deliver maximum value to the customer with minimal resources. This philosophy, often called lean thinking and grounded in the lean principle of maximizing productivity while minimizing waste, encourages organizations to view operations through customer value, ensuring every step in the production line contributes meaningfully.
Organizations often adopt a standard lean production model to structure their improvement efforts, but lean methods can be adapted to different industries and contexts. For a deeper dive into the principles and applications of lean methodologies, consider enrolling in the Lean Management Course, which offers comprehensive insights into implementing lean strategies effectively.
Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing
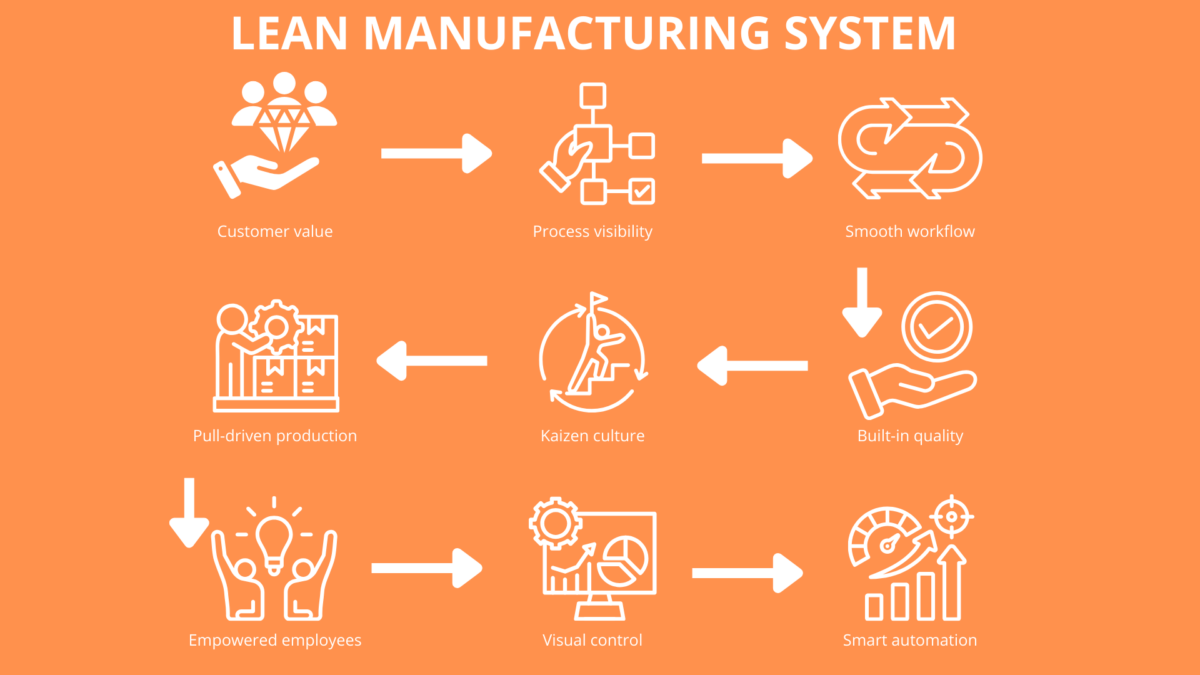
The foundation of lean manufacturing rests on five key principles:
- Define Value: Understand what the customer perceives as valuable.
- Map the Value Stream: Identify all steps in the value stream and eliminate those that do not add value, focusing on making value flow smoothly throughout the process.
- Create Flow: Ensure that the production process flows smoothly without interruptions, emphasizing the importance of continuous production flow as a core element of lean manufacturing.
- Establish Pull: Implement a pull system where production is based on actual customer demand.
- Pursue Perfection: Continuously seek ways to improve processes and banish waste from all operations.
These principles guide organizations in creating a lean enterprise that is responsive, efficient, and customer-focused.
Tools and Techniques in Lean Manufacturing
Implementing lean principles requires specific tools and techniques to identify inefficiencies and promote continuous improvement. Lean manufacturing techniques are essential for process improvement and optimization. Lean manufacturing offers a variety of tools and resources for organizations seeking to improve manufacturing processes, focusing on theoretical and practical aspects.
- Value Stream Mapping: A visual tool to analyze the flow of materials and information, helping to identify bottlenecks and areas of waste. This lean practice is crucial for visualizing and optimizing work processes, identifying waste, and improving workflow.
- 5S Methodology: This methodology focuses on workplace organization to improve efficiency and safety. The five steps—sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and sustain—create a foundation for a productive work environment.
- Inventory Management: Effective inventory management, such as using kanban cards and ERP integration, is vital in lean practice to reduce waste, minimize costs, and optimize warehouse space.
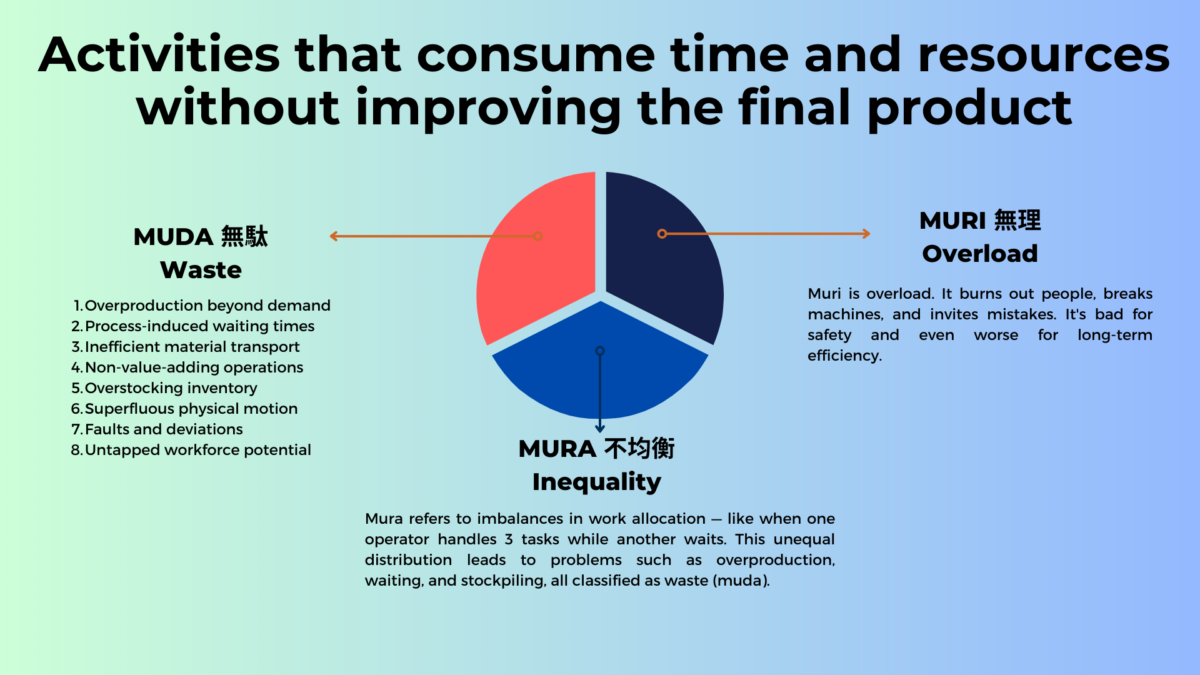
- Overprocessing: Identifying and eliminating overprocessing—unnecessary or excessive work that adds no value to the customer—is a key aspect of waste reduction in lean manufacturing.
Lean manufacturing techniques emphasize process improvement by continuously analyzing and refining the manufacturing process to eliminate waste and enhance productivity. While lean tools focus on streamlining workflows and reducing waste, manufacturing resource planning (MRP) systems offer a computer-based approach to manufacturing planning and control, focusing on inventory management and production scheduling within traditional manufacturing frameworks. Both approaches aim to improve manufacturing processes, but lean emphasizes waste elimination and optimization.
The Fundamentals of 5S Course provides practical guidance and implementation strategies for mastering the 5S methodology and enhancing workplace efficiency.
The Role of Continuous Improvement
At the heart of lean manufacturing lies the commitment to continuous improvement. This involves regularly assessing processes, seeking feedback, and making incremental changes to enhance performance. Cultivating a constant improvement culture is essential for achieving a meaningful and lasting difference in organizational performance, ensuring that organizations remain agile and responsive to changing demands.
For strategies on fostering a culture of ongoing enhancement, the Continuous Improvement Course offers valuable insights into building and sustaining improvement initiatives.
Implementing Lean in Manufacturing Operations
Implementing lean manufacturing requires a structured approach:
- Assessment: Evaluate current processes to identify areas of waste and inefficiency.
- Planning: Develop a roadmap for lean implementation, setting clear goals and metrics.
- Execution: Apply lean tools and principles to streamline operations, focusing on removing functional barriers and creating flow throughout the value stream.
- Review: Monitor progress and make adjustments as necessary to ensure continuous improvement. The goal is to achieve productive processes and develop a high-performance supplier network that supports operational excellence.
Effective implementation also hinges on strong leadership and teamwork. The Effective Teamwork and Leadership Course equips leaders with the skills to guide teams through lean transformations successfully.
Lean Manufacturing System: A Holistic Approach
A lean manufacturing system represents a comprehensive, organization-wide commitment to eliminating waste and maximizing customer value. Rather than focusing on isolated improvements, this approach examines the entire production process—from the initial sourcing of raw materials to the final delivery of products—to identify opportunities for streamlining and enhancement.
The lean manufacturing system is built on continuous improvement, respect for people, and a relentless focus on customer satisfaction. Implementing lean requires a cultural transformation, where every employee is encouraged and empowered to spot inefficiencies and contribute to process improvements. This collective effort is essential for sustaining meaningful and lasting change.
Key lean manufacturing tools, such as value stream mapping and total productive maintenance, play a vital role in this holistic approach. Value stream mapping helps organizations visualize the flow of materials and information, making pinpointing and eliminating wasteful steps easier. Total productive maintenance ensures that equipment is reliable and available, supporting smooth and efficient production processes.
Organizations can reduce waste, improve quality, and enhance customer satisfaction by adopting a lean manufacturing system. This long-term strategy drives operational excellence and creates a competitive edge in the marketplace by fostering a culture of continuous improvement and problem-solving at every level.
Optimizing the Supply Chain with Lean
Applying lean manufacturing principles to the supply chain unlocks significant opportunities to reduce waste and boost efficiency. Lean supply chain management involves scrutinizing every stage—from procurement of raw materials to the delivery of finished goods—to ensure a seamless flow of materials and information.
A key aspect of this approach is close collaboration with suppliers, which enables the implementation of just-in-time manufacturing. Organizations can minimize excess inventory and reduce lead times by synchronizing production with actual customer demand, resulting in a more agile and responsive supply chain.
Effective lean supply chain management requires open communication and strong stakeholder partnerships. This collaborative environment supports the elimination of bottlenecks, the reduction of unnecessary costs, and the improvement of overall quality. Organizations that embrace lean principles throughout their supply chain are better equipped to adapt to fluctuations in customer demand and mitigate the risks of disruptions.
Optimizing the supply chain with lean reduces waste and operational costs, enhances customer satisfaction, and strengthens the organization’s competitive position in the market.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction through Lean
Customer satisfaction is at the heart of lean manufacturing, guiding every improvement and innovation within the production process. Organizations can deliver products and services that truly add value by focusing on understanding and meeting customer needs.
Lean manufacturing principles, such as continuous improvement and respect for people, drive organizations to constantly refine their processes in pursuit of higher quality and greater efficiency. Tools like value stream mapping and systematic customer feedback collection enable companies to identify gaps between current performance and customer expectations, paving the way for targeted improvements.
Implementing lean principles in the production process leads to shorter lead times, more consistent quality, and greater responsiveness to customer demands. These improvements enhance customer satisfaction and foster loyalty and positive word-of-mouth, contributing to long-term business growth.
By making customer satisfaction a central goal, organizations can differentiate themselves in the marketplace, build a strong reputation, and secure a loyal customer base, ensuring sustained success in a competitive environment.
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing
Adopting lean manufacturing principles yields numerous advantages:
- Waste Reduction: Organizations can minimize unnecessary costs and improve resource utilization by eliminating and reducing waste.
- Enhanced Quality: Streamlined processes and optimized the production cycle lead to more consistent and higher-quality outputs.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Efficient operations enable faster delivery times and better responsiveness to customer needs.
- Increased Flexibility: Lean systems are more adaptable to changes in demand, and optimizing the production cycle enhances the organization’s competitiveness.
- Wealth Creation: Lean manufacturing helps organizations create wealth by maximizing value and efficiency throughout production.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are substantial, organizations may face challenges in adopting lean practices:
- Cultural Resistance: Shifting to a lean mindset requires changes in organizational culture and employee attitudes.
- Sustaining Improvements: Maintaining momentum in continuous improvement efforts demands ongoing commitment and monitoring.
- Training and Development: Ensuring all team members understand lean principles is crucial for successful implementation.
To address these challenges, investing in comprehensive training programs, such as the Effective Problem-Solving Course, can empower employees to identify issues proactively and develop practical solutions.
Conclusion
Embracing Lean MFG is a transformative journey that leads to more efficient, responsive, and customer-centric operations. Organizations can significantly enhance performance and competitiveness by understanding and applying lean principles, utilizing practical tools, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
For a holistic understanding and practical application of lean methodologies, explore the range of courses offered by Sabat Consulting:
- Lean Management Course
- Fundamentals of 5S Course
- Continuous Improvement Course
- Effective Teamwork and Leadership Course
- Effective Problem-Solving Course
Embark on your lean transformation today and position your organization for sustained success in the dynamic manufacturing landscape.


