Spis treści
What is a Lean Operation?
In today’s highly competitive and customer-driven economy, organizations constantly seek ways to optimize efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve product or service quality. Cost reduction is a key benefit of lean operations, as these strategies focus on eliminating waste and streamlining processes. One of the most effective approaches to achieving these goals is through Lean Operations, which helps organizations reduce costs while enhancing overall performance. But what exactly does this term mean, and how can businesses successfully implement it to achieve sustainable growth?
Understanding Lean Operations
A lean operation systematically manages and improves processes by eliminating waste, optimizing resources, and focusing on creating customer value. Lean operations aim to create customer value by streamlining processes and efficiently meeting customer needs. Rooted in the Toyota Production System, this systematic method is based on lean methodology, which seeks to streamline work, reduce inefficiencies, and deliver what the customer wants, when they want it, using the least resources necessary.
At the core of lean operations is the idea of doing more with less—less time, space, human effort, equipment, and materials—while still meeting customer demand with high quality and speed.
Key Objectives of Lean Operations:
- Eliminate waste in all forms.
- Waste reduction through systematic elimination of inefficiencies and unnecessary processes.
- Streamline internal processes.
- Improve customer satisfaction.
- Reduce operational costs.
- Achieve continuous improvement.
If you’re ready to implement these principles practically in your organization, check out our Lean Management course for hands-on strategies backed by 25 years of experience.
The Principles of Lean Operations
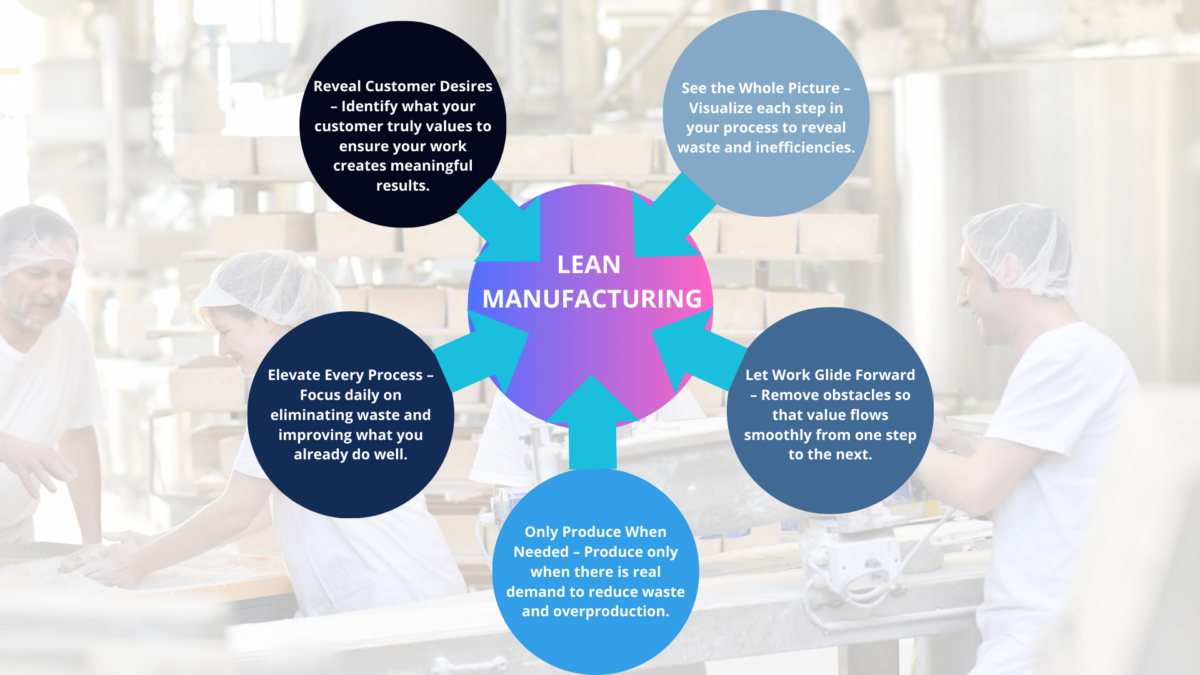
Five core principles guide lean operations. In addition to these principles, lean operations should be considered a core value, deeply embedded in the company culture and identity.
1. Define Value
Value is defined from the perspective of the end customer. What are they willing to pay for? What truly meets their needs?
2. Map the Value Stream
Value stream mapping involves analyzing the flow of materials and information required to bring a product or service to the customer. This visual tool helps identify waste and areas for improvement across the entire value stream, supporting waste reduction through targeted process improvements.
3. Create Flow
Processes should be organized to ensure a continuous flow of value, emphasizing the importance of achieving a smooth flow in all processes. Interruptions, delays, and bottlenecks must be identified and eliminated.
4. Establish Pull
A pull system ensures that nothing is made or moved until there is actual customer demand, reducing excess inventory and overproduction and helping to minimize storage costs.
5. Seek Perfection
Through continuous improvement (Kaizen), organizations strive to eliminate waste, improve flow, and enhance quality.
For a deeper understanding of continuous improvement principles, we recommend our course on Continuous Improvement.
Customer Value and Satisfaction
At the heart of lean operations lies a relentless focus on customer value. Lean management is built on the principle that every process and activity should contribute to creating value for the customer—anything that does not is considered waste and should be eliminated. By understanding customer needs and expectations, organizations can tailor their production process to deliver products and services that truly meet those needs, exactly when and how the customer wants them.
Lean operations management leverages tools like value stream mapping to visualize and analyze the entire value stream, identifying opportunities to eliminate waste and streamline operations. This approach ensures that every step in the process adds value for the customer, resulting in a smoother, more efficient workflow.
A key lean management technique is the pull system, which aligns production with customer demand. Instead of producing goods based on forecasts, the pull system ensures that work is only initiated in response to real customer orders, reducing excess inventory and minimizing waste. This just-in-time approach improves efficiency and enhances customer satisfaction by delivering precisely what is needed, when it is required.
Continuous improvement is another cornerstone of the lean approach. Companies can maximize customer value, improve efficiency, and maintain high-quality standards by regularly assessing and refining the production process. Organizations that adopt a lean mindset and prioritize customer value often see significant improvements in customer satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term growth.
By focusing on eliminating waste, optimizing the value stream, and responding to actual customer demand, lean operations empower businesses to deliver greater value for the customer, driving both operational excellence and business success.
Lean Operations vs. Traditional Operations
Traditional operations often rely on forecasts and large batch production. Lean operations, on the other hand, focus on:
- Just-in-time manufacturing
- Lean tools such as 5S, Kanban, and value stream mapping
- Minimize waste in all forms: overproduction, waiting, excess inventory, defects, motion, overprocessing, and underutilized talent.
- Customer value as the guiding principle
Implementing Lean Operations
Implementing lean operations involves a shift in mindset and culture. It’s not just about tools; it’s about transforming how work is done. Lean transformation is a process of organizational change that requires careful change management and active involvement from all company levels. Employee empowerment is essential in supporting successful lean transformation, as it fosters a positive corporate culture and encourages teams to participate, communicate, and innovate.
Steps to Implement Lean Operations:
- Train employees in lean principles and lean thinking.
- Conduct a thorough value stream analysis.
- Identify and eliminate inefficient processes.
- Standardize work processes for consistency.
- Use lean tools like 5S, Kanban, and A3 problem-solving.
- Foster a lean culture that supports change.
👉 Want to see real-life applications of these concepts? Our Lean Management course will show you how to embed these principles in your day-to-day operations.
Benefits of Lean Operations
Organizations that embrace lean operations can expect:
- Reduced waste and lower operational costs
- Improved efficiency, increased efficiency, and process reliability
- Higher customer satisfaction
- Empowered employees through involvement and ownership
- More sustainable solutions
The automotive industry is a classic example of lean success, but today, lean is also used in call centers, healthcare, construction, and service-based businesses.
Lean Operations Management: The Strategic Layer
Lean operations management involves integrating lean practices into strategic decisions. This includes aligning lean initiatives with the company’s mission and long-term objectives. Implementing a lean management system is crucial for optimizing internal processes, reducing waste, and building business agility. It ensures that lean becomes part of the organization’s DNA. The concept of a lean enterprise highlights integrating lean principles across all core operations, such as procurement, logistics, and accounting, to foster a cohesive, waste-reducing culture.
Lean operations management delivers consistent and scalable results by focusing on streamlining operations, customer demand, and performance improvement. Supply chain optimization is also key, supporting waste reduction and continuous organizational improvement.
Key Lean Tools and Techniques
- 5S – A system for organizing workplace cleanliness and efficiency.
- Kanban – A scheduling system that supports pull production.
- A3 Thinking – A lean initiative that uses a structured problem-solving and process improvement approach.
- Poka-Yoke – Error-proofing mechanisms.
- Andon Systems – Visual feedback systems.
Want to implement 5S in your workplace? Discover how in our 5S Training Course.
Industry Applications of Lean
Lean operations are not limited to the manufacturing floor—they have transformed a wide range of industries by helping organizations eliminate waste, streamline processes, and enhance efficiency. The automotive industry, particularly through the pioneering efforts of companies like Toyota, has long been recognized for its successful adoption of lean manufacturing techniques such as value stream mapping and kaizen events. These methods have significantly improved production processes, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Beyond automotive, lean principles have been widely embraced in healthcare, where they are used to optimize clinical and administrative processes, improve patient flow, and reduce unnecessary steps that do not add value for the patient. In the construction industry, lean operations management helps teams improve project management, minimize delays, and reduce material waste, resulting in more efficient and cost-effective projects.
Service industries, including call centers, have benefited from the lean approach. By applying lean tools to administrative processes, these organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce wait times, and improve customer experience. Value stream mapping and other lean manufacturing techniques are adapted to fit the unique challenges of each sector, always to create value for the customer and eliminate waste.
No matter the industry, implementing lean operations significantly improves efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. By adopting a lean mindset and focusing on continuous improvement, companies can remain competitive, drive growth, and deliver exceptional customer value.
Lean Culture: Sustaining the Change
Without a supportive lean culture, even the best systems can fail. Culture shapes behaviors, decision-making, and openness to change. Leaders must model lean behaviors, encourage experimentation, and recognize improvements.
Explore how effective teamwork and leadership can strengthen your lean culture in our Teamwork and Leadership course.
Measuring Lean Operation Success
Measuring their effectiveness using clear, actionable metrics ensures that lean operations deliver the desired results. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as lead time, throughput, and inventory levels provide valuable insights into how well the lean approach works within the organization. Monitoring these metrics helps identify bottlenecks, track progress, and highlight areas where further improvements can be made.
Customer satisfaction is another critical measure of lean success. Companies can assess how well their lean initiatives meet customer needs and expectations by regularly gathering feedback and tracking quality metrics. Employee engagement is also an important indicator, as empowered and involved employees are vital to sustaining a culture of continuous improvement.
Value stream mapping plays a central role in measuring lean operation success. By visualizing the entire value stream, organizations can pinpoint inefficiencies, set improvement targets, and monitor the impact of lean tools and techniques over time. Kaizen events, root cause analysis, and other lean initiatives provide additional opportunities to assess progress and drive ongoing performance improvement.
Benchmarking against industry leaders and conducting regular reviews of lean operations ensures that organizations stay on track and continue to evolve their lean practices. By consistently measuring and refining their approach, companies can achieve lasting results, maximize value for the customer, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Common Pitfalls in Lean Implementation
- Focusing only on tools, not on mindset
- Lack of leadership support
- Poor communication
- Inadequate training
- Not involving frontline employees
That’s why a structured, experience-based approach is vital. Our Lean Management course is grounded in real-world examples, not just theory.
Lean in Problem Solving
Lean thinking also revolutionizes how organizations approach problems. Instead of quick fixes, lean encourages root cause analysis, structured decision-making, and measurable follow-ups.
Learn a proven method in our Problem Solving course.
🎓 Ready to Master Lean Manufacturing the Practical Way?
Enroll in our Lean Management course to move beyond theory and apply lean manufacturing principles across different industries. This program has actionable insights from over 25 years of experience implementing Lean and 5S in diverse organizational settings.
🎥 You can preview one of the lessons for free to see how practical and hands-on this course is.
🎮 If you’re looking for a more engaging way to learn, check out our simulation-based training: the GET LEAN Simulation Game—a powerful tool for reinforcing Lean concepts through interactive learning.